Introduction
The 2022 Ontario Economic Outlook and Fiscal Review includes the government’s Building Ontario Progress Report. This report provides an update on the government’s progress to deliver on Ontario’s Plan to Build.
Building Ontario’s Economy — Progress Report
Building Ontario’s Economy
Ontario is unleashing the economic potential of critical minerals, including in the Ring of Fire. Ontario is getting this done by:
- Releasing its first-ever Critical Minerals Strategy in March 2022, which focuses on priorities that will support better supply chain connections between industries, resources and workers in Northern Ontario and manufacturing in Southern Ontario.
- Committing close to $1 billion to support critical legacy infrastructure such as all‐season roads to the Ring of Fire.
- Supporting the ongoing Environmental Assessments, led by Marten Falls First Nation and Webequie First Nation, for both the Marten Falls Community Access Road and the Webequie Supply Road.
- In April 2022, Marten Falls First Nation and Webequie First Nation, as co-proponents, also submitted to Ontario the proposed Terms of Reference for the Northern Road Link Environmental Assessment. Should the Terms of Reference receive approval, they would begin the Environmental Assessment for the Northern Road Link.
- Ontario expects the federal government to be a full partner for the Ring of Fire, respect provincial jurisdiction and, at minimum, match Ontario’s investments to support critical infrastructure in seizing this generational opportunity.
- Announcing a $12 million investment to extend the Ontario Junior Exploration Program (OJEP) for an additional two years. The program will continue to help cover eligible costs for junior exploration companies searching for potential mineral deposits.
- Announcing the creation of a Critical Minerals Stream for the OJEP, supported by an investment of $4 million per year over the next three years, to help ensure that the OJEP supports critical minerals projects, in addition to those focused on precious metals.
- Committing $5 million to develop the Critical Minerals Innovation Fund to support organizations pursuing innovative projects that develop new technologies and attract private‐sector investments focused on extracting and processing critical minerals.
- Announcing the Northern Ontario Regional Technology Development Site in April 2022, a public and private sector collaboration that will connect Ontario’s manufacturing sector with Northern Ontario’s mining and mineral expertise, talent and leadership.
Transforming Ontario’s Electric Vehicle Supply Chain

The government is helping transform the auto sector so it can build the cars and batteries of the future. Ontario is getting this done by:
- Attracting $16 billion in transformative automotive investments by global automakers and suppliers of EV batteries and battery materials over the last two years. This supports the government’s goal to maintain and grow Ontario’s auto sector by building at least 400,000 electric and hybrid vehicles by 2030. The most recent of these investments include:
- In July 2022, Umicore, a multinational circular materials technology company based in Belgium announced a $1.5 billion investment to build a first-of-its-kind, industrial scale cathode and precursor materials manufacturing plant in Eastern Ontario with operations planned to commence in late 2025. These components are critical in the production of EV batteries, and this investment would further connect critical minerals in the North to EVs and EV battery manufacturers in Southern Ontario.
- In May 2022, Stellantis announced a $3.6 billion investment to retool and modernize its Windsor and Brampton plants, converting them to flexible, multi-energy vehicle assembly facilities ready to produce EVs. The company will also build two new research and development centres focusing on EVs and EV battery technology. Ontario is supporting these critical investments with up to $513 million in support.
- In April 2022, General Motors announced an investment of more than $2 billion to transform the company’s Oshawa and Ingersoll manufacturing facilities to deliver the company’s next generation of vehicles, including GM’s new all‐electric commercial vehicle brand, BrightDrop, with the Ontario government providing up to $259 million in support.
- In March 2022, LG Energy Solution and Stellantis announced the largest auto investment in Ontario’s history. This joint investment of more than $5 billion will be used to build the province’s first large‐scale EV battery manufacturing plant in Windsor, supported by the Ontario government. Production operations are planned to launch in the first quarter of 2024 with the facility expected to be fully operational by 2025 and employing an estimated 2,500 people.
Forging Ontario Made Clean Steel

The government’s plan to support the transformation of the province’s automotive supply chain to build the cars of the future includes supporting the shift to low-carbon steel production. This shift will give Ontario a competitive advantage in attracting game-changing investments and create and retain skilled local jobs for Ontario workers. Ontario is supporting low-carbon steel production by attracting the following investments:
- ArcelorMittal Dofasco’s $1.8 billion investment in Hamilton to replace its coal‐fed coke ovens and blast furnaces with a new hydrogen-ready direct reduced iron fed electric arc furnace (EAF), which broke ground in October 2022. Ontario is contributing up to $500 million towards the project, which will support the livelihoods of 4,600 people working at the facility and is expected to be completed by 2028. The project will reduce greenhouse gas emissions by about three million tonnes annually, the equivalent of taking almost one million cars off the road and will help move the province towards its goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 30 per cent by 2030.
- Algoma Steel’s $700 million investment, announced in November 2021, in an all‐new, low‐emission EAF that will help lay the foundation for economic prosperity, and new, well‐paying jobs in Sault Ste. Marie and across all of Northern Ontario. The investment into an EAF will reduce carbon emissions by approximately 70 per cent at the facility. The construction of the transformative EAF project continues on time towards a targeted start up in 2024.
Powering Ontario: Supporting the Pickering Nuclear Generating Station’s Continued Operations
Ontario is taking action to ensure its energy system is clean, reliable and affordable to support a growing population and economy. This is essential as Ontario attracts investments in manufacturing and mining, in sectors such as electric vehicles and batteries, to compete and support the transition to a clean economy.
Ontario is supporting Ontario Power Generation’s (OPG) continued safe operation of the Pickering Nuclear Generating Station (NGS). Under the OPG proposal, which is subject to Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) approval, electricity generation at Pickering “B”, units five to eight of the Pickering NGS, would end in September 2026.
- The six units of the Pickering NGS currently account for about 14 per cent of Ontario’s electricity needs.
- OPG employs approximately 4,500 staff for its Pickering nuclear operations. In total, there are about 7,500 jobs across Ontario related to the Pickering NGS.
- With strong economic growth and significant electrification of industry and uptake of electric vehicles forecasted over the coming decades, the government has also asked OPG to update its feasibility assessment for refurbishing the four Pickering “B” units of the Pickering NGS. Refurbishment of the Pickering NGS could result in an additional 30 years of reliable, clean, safe and zero-emissions electricity from the facility.
Advancing Small Modular Reactors
In March 2022, the governments of Ontario, Saskatchewan, New Brunswick and Alberta agreed to a joint strategic plan outlining the path forward on small modular reactors (SMRs), including milestones for SMR deployment.
- The deployment of one 300 MW SMR at OPG’s Darlington Nuclear site, as early as 2028, subject to appropriate approvals, would be Canada’s first commercial, grid-scale SMR and could displace 0.3 to 2 megatonnes of CO2 emissions per year. This clean energy project will stimulate the creation of high-quality jobs in Ontario’s nuclear sector, leverage a strong Ontario-based supply chain, and drive economic growth across the province.
Supporting Growth in Ontario’s Hydrogen Sector
Through Ontario’s low-carbon hydrogen strategy, the government is leveraging the province’s strengths, such as clean electricity, to develop a low-carbon hydrogen economy in Ontario that will create jobs, attract investment and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- The hydrogen strategy identifies innovative projects that can help secure a clean energy future with hydrogen playing a critical role as a clean and safe energy source.
- For example, in April 2022, Atura Power, a subsidiary of Ontario Power Generation, announced the Niagara Hydrogen Centre as its first site for large-scale hydrogen production. The final investment decision is expected in 2022, pending an award of federal funding.
Developing a New Program for Small Hydroelectric Facilities
Small hydroelectric power dams play an important role in Ontario, both in generating clean, renewable electricity and providing benefits such as recreational opportunities, flood control, irrigation, tourism and supporting local employment and economic development.
- The Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) is developing a potential program to provide new contracts for existing small hydroelectric generation facilities (i.e., with capacity under 10 megawatts), as requested by the government. The IESO is to report back on the implications of potentially launching a program by July 31, 2023, subject to a potential directive from the Minister of Energy.
Ensuring a Reliable, Affordable and Clean Energy Supply
The government has directed the Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) to acquire 4,000 MW of new electricity generation and storage resources to meet emerging energy needs and ensure a reliable, affordable and clean electricity supply.
- Acting on the advice of the IESO to provide for reliable electricity supply, these energy procurements will acquire at least 1,500 MW of stand-alone energy storage resources, up to 1,500 MW of natural gas generation, with the remainder coming from other resources.
Manufacturing Critical Medical Supplies to Protect Ontario
The government is supporting local innovators and businesses to further enhance Ontario’s domestic supply chain capacity. Ontario is getting this done by:
- Passing the Pandemic and Emergency Preparedness Act, 2022, to help ensure that Ontario’s public services, and especially its critical frontline workers providing essential services, have a robust ongoing centralized supply chain for personal protective equipment (PPE) as well as other critical medical supplies and equipment. As of February 17, 2022, over 92 per cent of the government’s forecasted investment in PPE for the next 18 months will be with Ontario or Canadian-based manufacturers.
- Enhancing Ontario’s domestic supply chain capacity and building up the life sciences and manufacturing sector to ensure the province is well-prepared for future challenges by making investments through the Ontario Together Fund. As of September 30, 2022, Ontario has announced a total commitment of more than $78 million through the Ontario Together Fund to support 61 companies and 11 organizations in supplying emergency products, as well as other solutions to build resilience in the health care sector.
- Investing $23.3 million to support 3M Canada’s capital investment of $70 million to expand its Brockville, Ontario manufacturing facility to produce Ontario-made N95 respirators. The N95 respirators started rolling off the production line as of April 2021 to provide frontline workers with the protection they need in the continued fight against COVID‑19 and ensure Ontario and the rest of Canada have a reliable supply in the event of any future outbreaks. The Government of Canada made a matching investment towards 3M Canada’s project.
Supporting Innovation and New Technologies
Cultivating innovation is more important than ever for robust long-term economic growth and job creation. Ontario is supporting the province’s innovation and technology ecosystem by:
- Investing nearly $107 million in new critical technology initiatives to both support access to and drive commercialization of technologies that will help support the next generation of innovation.
- Investing $15 million over three years in a new Life Sciences Innovation Program to help entrepreneurs develop and scale innovative technologies in the life sciences sector. In addition, the government released its new life sciences strategy, Taking Life Sciences to the Next Level, which sets a plan to make Ontario a global hub for biomanufacturing and life sciences. To support the next phase of the strategy, the government is establishing a forward-looking life sciences council. The council will help tackle challenges and barriers for Ontario companies, innovators and entrepreneurs.
Attracting Businesses Through Invest Ontario
Given the increasing global competition among jurisdictions to attract business investments, the government is positioning Ontario as a top-tier destination for investment and job creation. The government is sending a strong signal to investors that Ontario is open for business.
To support this, the Ontario government has established Invest Ontario, the province’s investment attraction agency, which is providing access to services for businesses looking to invest in the province. This includes insight and intelligence on business and market opportunities; talent support to help employees settle in Ontario and training partnerships with universities and colleges; facilitated access to all levels of government and local service providers; as well as financial assistance through the $400 million Invest Ontario Fund. Examples of success include:
- Invest Ontario worked with Johnson & Johnson Inc. to help secure an investment of nearly $15 million in the company’s current pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities in Guelph, supported by a $2.5 million investment through the Ontario Together Fund.
- Through Invest Ontario, the government will provide up to $40 million in support to help create the OmniaBio Inc. cell and gene therapy manufacturing facility in Hamilton.
Attracting Investment, Opportunity and Jobs
Making Ontario open for investment and jobs means making Ontario the best place to open and grow a business. Cutting red tape, lowering energy costs and supporting the investments of new and growing businesses across the province will help them thrive today and tomorrow.
Lowering Business Costs
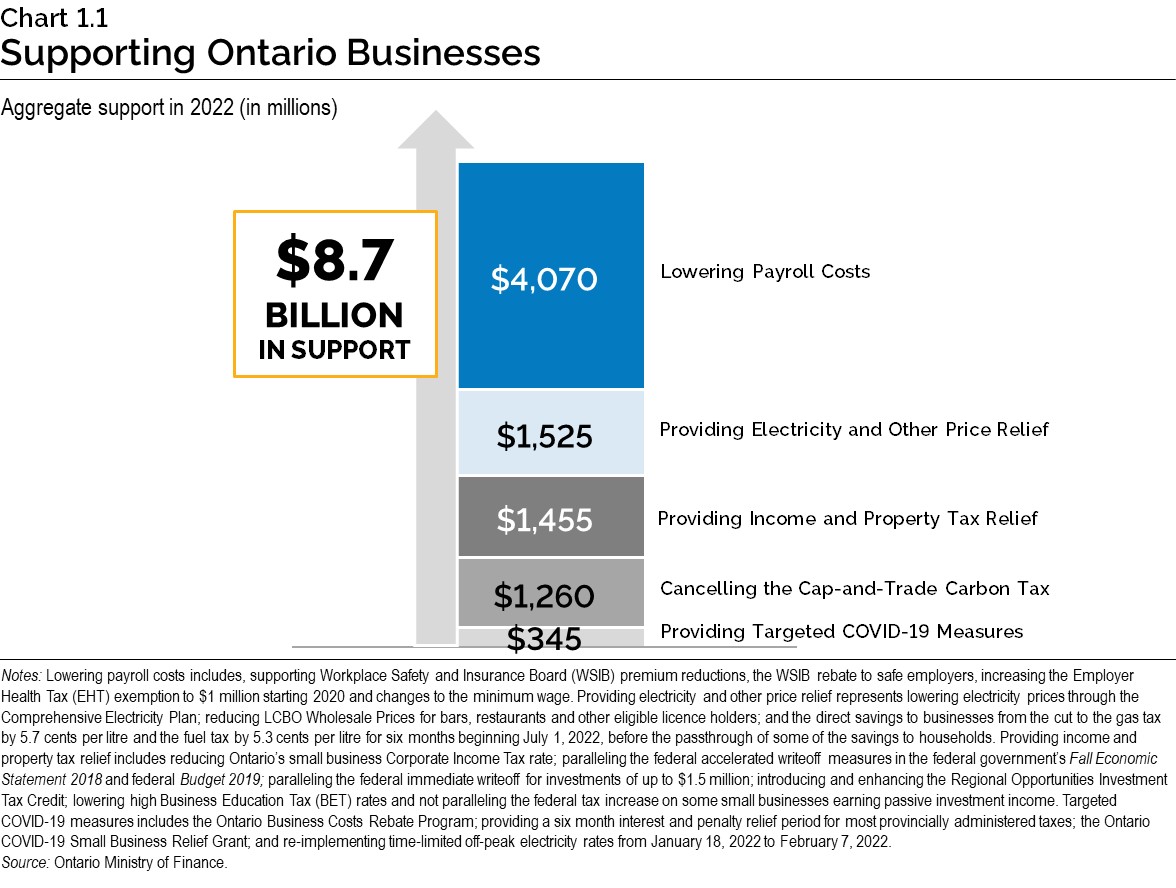
Since June 2018, the government has taken significant actions to lower costs for businesses. These actions continue to support businesses today and contribute to a competitive economic environment that will attract investment and create opportunities for the future. In 2022, the government is supporting an estimated $8.7 billion in cost savings and support for Ontario businesses, with $4.0 billion going to small businesses. Some of these actions include:
- Supporting a reduction in Workplace Safety and Insurance Board (WSIB) premiums and the WSIB rebate without reducing benefits;
- Increasing the Employer Health Tax (EHT) exemption from $490,000 to $1 million;
- Cancelling the cap-and-trade carbon tax;
- Allowing businesses to accelerate writeoffs of capital investments for tax purposes, including immediate expensing of up to $1.5 million annually for eligible capital investments;
- Lowering high Business Education Tax (BET) rates by $450 million for over 200,000 employers, or 94 per cent of all business properties in Ontario;
- Reducing the small business Corporate Income Tax rate to 3.2 per cent;
- Introducing and temporarily enhancing the Regional Opportunities Investment Tax Credit to encourage investments in regions of Ontario that have lagged in employment growth;
- Lowering electricity costs by 15 to 17 per cent in 2022 for medium-size and larger commercial and industrial customers under the Comprehensive Electricity Plan;
- Cutting the gas tax by 5.7 cents per litre and the fuel tax by 5.3 cents per litre beginning
July 1, 2022; and - Providing a deeper wholesale discount on the cost of alcohol purchased from the Liquor Control Board of Ontario (LCBO) for bars, restaurants and other eligible licence holders.
Building Ontario’s Workforce — Progress Report
Preparing Students for the Jobs of the Future
Ontario students should have the best learning experiences and opportunities to be prepared for the jobs of tomorrow. Through a modernized curriculum, new and enhanced programs related to entrepreneurship, skilled trades, and science and technology, as well as more hands-on learning opportunities, students will have the essential skills and support for whatever path they choose.
A Plan to Help Students Catch Up
After two years of COVID‑19 pandemic disruptions, Ontario has launched its Plan to Catch Up, which is focused on keeping students in classrooms from September until June, providing students with the best learning experience possible and preparing them with the skills they need for the jobs of tomorrow. Students and educators are already benefiting from the key investments of this plan, which include:
- Keeping students in classrooms full time, with the complete school experience that includes extra-curriculars like clubs, sports, band and field trips;
- Expanding student supports for tutoring, literacy and special education;
- Modernizing Ontario’s curriculum, including in the skilled trades and STEM-related courses;
- Providing more money to build schools and improve education; and
- Helping students with historic funding for mental health supports.
Emphasizing STEM Education Across All Grades
The government has continued to overhaul Ontario’s curriculum with a focus on labour market needs, mandating learning on financial literacy, coding, entrepreneurship and leadership development. These courses will ensure the next generation of Ontario graduates are getting the education they need to succeed.
- Introduced in the 2022–23 school year, the new Ontario science and technology curriculum emphasizes real-world connections between STEM across Grades 1 to 9 and includes learning on coding, emerging technology and skilled trades.
- The math curriculum for students in Grades 1 to 9 was also updated to include new learning on data literacy, mathematical modelling and an emphasis on financial literacy.
- In addition, to help students build the skills and confidence they need to excel, the government has de-streamed all Grade 9 courses, which began with the Grade 9 math course in 2021–22.
Building a Pipeline of Job-Ready Graduates
Ontario is expanding the degrees that publicly assisted colleges in Ontario can offer, including new, three‐year applied degrees and additional four‐year degree programs in key in-demand sectors. Some examples of three-year applied degree programs that are being considered or are under development include a Bachelor of Skilled Trades Business Management and a Bachelor of Computer Science.
Building a Skilled Workforce
The Ontario government is working to fill labour shortages and help build the critical infrastructure the province needs, including highways, transit, schools, housing and hospitals. To do this, the province is modernizing the apprenticeship and skilled trades system, attracting skilled newcomers and investing in skills training.
Helping More People Learn a Trade in Ontario
Many tradespeople in Ontario will be retiring2 in the coming years creating an even greater need for new apprentices. The government of Ontario is working to address the acute labour shortage in the skilled trades and ensure that Ontario has the workers it needs.
- The government launched a Skilled Trades Strategy, announced in the 2020 Budget, to break the stigma associated with the skilled trades, simplify the system and encourage employer participation in sponsoring and hiring trained apprentices.
- The Skills Development Fund supports innovative training projects that upskill workers and job seekers, including apprentices, preparing them for meaningful careers. The first two rounds of funding through the Skills Development Fund delivered 388 training projects, helping more than 393,000 workers take the next step in their careers in in-demand industries, including carpenters, plumbers and health care workers. For more details on the latest round of funding, see Chapter 1, Section B: Enhancing Ontario’s Plan to Build.
Making It Easier for Skilled Workers To Come Work and Live in Ontario
The government is helping to ensure the success of newcomers in Ontario’s labour market:
- Out of province workers in over 30 in-demand professions such as engineers, auto mechanics, plumbers, as well as other regulated professionals and tradespeople can get their credentials processed within a service standard of 30 business days.
- Ontario is the first province in Canada to introduce legislation that removes Canadian work experience for internationally trained professionals in the regulated professions. Ontario is also recognizing three fuel‐related professions under the province’s skilled trades legislation, meaning the government will be officially recognizing all 55 Red Seal trades.
- Ontario is supporting apprentices from other provinces to continue their training in Ontario, by working with Skilled Trades Ontario to harmonize training standards for a dozen trades.
Enhancing the Ontario Immigrant Nominee Program
In the 2022 Budget, the government invested an additional $15.1 million over three years to help the Ontario Immigrant Nominee Program welcome more newcomers. This builds on the two-year entrepreneurship pilot that was launched in 2021 to attract 100 international entrepreneurs to start or to grow businesses in regions outside of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA).
Expanding Training to More Workers Through Better Jobs Ontario
The government relaunched the former Second Career program as Better Jobs Ontario as part of the 2022 Budget. Since January 2021, 6,195 people have started training through Better Jobs Ontario (as of August 31, 2022).
Better Jobs Ontario was also expanded to support a larger, more diverse range of workers who may face challenges finding stable jobs, including gig workers, youth, newcomers, justice-involved people and those on social assistance.
Transforming Employment Services
Ontario is launching the next phase of its integrated employment services system to help more job seekers and people on social assistance in York, Halton, Stratford-Bruce Peninsula and Kingston-Pembroke. This new approach will be implemented provincewide by the end of 2023.
This initiative builds on the successes of the first three regions — Peel, Hamilton-Niagara and Muskoka-Kawarthas — which began in 2020 and has already helped more than 52,000 people find a path to employment. Early success of the initial regions has 84 per cent of workers in gainful employment whereas the previous system had fewer than one per cent success in finding employment.
Ontario Jobs Training Tax Credit
The government introduced a temporary Ontario Jobs Training Tax Credit for 2021 and 2022 that provides up to $2,000 in relief for 50 per cent of a person’s eligible training expenses for the year, such as tuition at an eligible Canadian institution and fees paid to certain bodies in respect of an occupational examination. The credit is refundable, meaning that people can benefit whether or not they owe any Ontario Personal Income Tax.
The 2022 credit will provide an estimated $275 million in support to about 240,000 people, or $1,150, on average.
Supports for Workers
The government is supporting workers by helping them earn bigger paycheques, providing better protections and more foundational rights to keep workers and the public safe.
Raising the Minimum Wage
On October 1, 2022, the government increased the general minimum wage to $15.50 per hour. This is the second increase since January 2022, which brings the total increase in the general minimum wage to eight per cent over one year, helping workers keep up with rising costs. The majority (58.3 per cent) who are benefiting are women. The minimum wage will continue to rise, with the next increase amount to be announced in April 2023.
The government removed the lower minimum wage rate for liquor servers and raised the wage rates for the other special minimum wage categories proportionally to the increase in the general minimum wage. With this increase, Ontario’s minimum wage is among the highest in the country.
Supporting Digital Platform Workers
As part of the Working for Workers Act, 2022, Ontario is the first province in Canada that entitled digital platform workers to earn at least the general minimum wage for time worked and provided them with other foundational rights and protections, including:
- The right to keep their tips, along with regular pay periods;
- The right to information and clarity around algorithms on how pay is calculated and how and why a worker might be penalized in the allocation of work;
- Protection from arbitrary deactivation, with advance written notice if they are being removed from the platform and why;
- The right to resolve their work-related disputes in Ontario; and
- Full Employment Standards Act reprisal protection for all workers when they seek to assert their rights.
Building Ontario’s Health Care Workforce
Ontario’s dedicated health care workers are the foundation of the province’s health care system. The government is building a stronger health care workforce to provide Ontario’s nurses, doctors, personal support workers and other health care professionals with the resources, support and guidance they need to provide quality care to the people of Ontario. Measures include:
- In August 2022, the Ontario government introduced its Plan to Stay Open: Health System Stability and Recovery, a five-point plan to provide the best care possible to patients and residents. When fully implemented, this plan is expected to add up to 6,000 additional health care workers. This is in addition to over 11,700 health care workers, including nurses and personal support workers, already added to the health system since winter 2020.
- Since January 2022, over 800 internationally educated nurses have become licensed as nurses in Ontario through government funded programming. The province anticipates that by March 2023 over 1,000 international nurses will gain the practice and language requirements necessary to work in Ontario.
- The 2022 Budget announced a suite of initiatives to bolster the province’s health care workforce, including $230 million in 2022–23 to enhance health care capacity in hospitals. This investment supports thousands of hospital staff including over 4,500 externs and 2,300 nurses. It also has provided over 300,000 additional hours of physician coverage in rural, remote and in-need hospitals.
- The 2022 Budget also introduced a permanent wage enhancement for personal support workers (PSWs) and direct support workers (DSWs) by investing approximately $2.8 billion over three years. This investment supports over 158,000 PSWs and DSWs who provide publicly funded services in hospitals, long‐term care, home and community care and social services.
- Starting in spring 2023, Ontario will expand the Learn and Stay Grant for approximately 2,500 eligible postsecondary students who enrol in a high-priority program, such as nursing, in a high‑priority community, and commit to work in an underserved community in the region where they studied after graduation.
- Investing in the students of today who will become the skilled health care professionals of tomorrow is a key element of Ontario’s plan to strengthen the health care system across the province. This is why the government has invested:
- $145.5 million to increase the number of nurse education seats by 1,500 which will add 2,000 nurses to the system by 2025–26;
- Over $400,000 in a one-time increase to train an additional 38 nurse practitioners starting in 2022–23; and
- $42.5 million over two years beginning in 2023–24 to support the expansion of undergraduate and postgraduate medical education and training in Ontario. This expansion is the largest of its kind in over 10 years and will result in an increase of 160 undergraduate seats and 295 postgraduate positions over the next five years.
Building Infrastructure — Progress Report
Building Ontario
The government is moving forward with one of the most ambitious capital plans in Ontario’s history, including plans to build highways, hospitals, broadband and public transit. Thousands of infrastructure projects are in planning or under construction across Ontario, from Timmins to Niagara, from Brampton to Windsor, from Durham Region to Simcoe County, from Pembroke to Pickering. These projects will get drivers out of gridlock, connect communities to high-speed internet and lay the foundation for future prosperity.
Fighting Gridlock
People in Ontario depend on a reliable and effective transportation system to get them to and from work, home to their families, provide better connections to housing, and to keep goods moving across the province. Gridlock on highways and roads costs the economy more than $11 billion a year in productivity, including time lost by commuters and drivers, higher costs of doing business and reduced access to jobs and surrounding areas. Ontario is building highways, roads, bridges and public transit that will support growth and help relieve gridlock.
Building Roads, Highways and Bridges Across Ontario
Ontario undertakes approximately 250 highway rehabilitation construction projects annually. In 2022–23 Ontario is investing $3.0 billion to repair and expand provincial highways and bridges. These targeted investments are estimated to create or sustain approximately 15,700 direct and indirect jobs and improve quality of life for workers, families and small businesses across Ontario.
Table 1.1
Recently Completed Highway Projects
Northern
- Highway 11 in Fauquier: Replaced the Groundhog River Bridge.
- Highway 11 in North Bay: Resurfaced pavement and improvements south of the north junction of Highway 17/11B.
- Highway 579 north of Cochrane: Replaced the Gilles Creek Bridge.
Eastern
- Highway 401 in Brighton: Improved interchange, including ramp and road realignments and traffic signals at County Road 30.
- Highway 417 in Ottawa: Highway widening and bridge rehabilitation from Maitland Avenue to Island Park Drive.
- Highway 17 in Renfrew: Rehabilitation and resurfacing work from Scheel Drive to Bruce Street.
Southwestern
- Highway 40 in Lambton: Resurfacing work from Wallaceburg to Stanley Line.
- Highway 6 in Northern Bruce Peninsula: Resurfacing work from Miller Lake to Tobermory.
- Highway 402 in Lambton: Resurfacing work from Lambton Road 79 to Hickory Drive.
Central
- QEW in Niagara: Constructed the first-ever diverging diamond interchange in Ontario at Glendale Avenue.
- Highway 401 in Oshawa: Replaced and rehabilitated the Oshawa Creek Bridge.
- Highway 12 in Simcoe: Upgraded traffic signals to improve safety at Triple Bay Road and Rumney Road.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Transportation.
Ontario is investing $25.1 billion over the next 10 years to connect communities, fight gridlock and keep goods and people moving across the province. This includes work on key corridors such as the QEW and Highway 7:
- The QEW Garden City Skyway rehabilitation project includes a new twin bridge on the QEW over the Welland Canal connecting the City of St. Catharines to the Town of Niagara-on-the-Lake. This section of the highway supports the province’s supply chain by linking the international border crossings at Niagara Falls and Fort Erie with the Greater Golden Horseshoe.
- The next phase of construction for the new Highway 7 between Kitchener and Guelph will provide relief to the gridlocked Highway 401 and connect the fast-growing urban centres of Kitchener, Waterloo and Guelph. Design of the Frederick Street bridge replacement is well underway with utility work targeted to begin in spring 2023.
Ontario’s highway plan also includes widening existing corridors to increase capacity and enhance road safety for travellers by separating opposing traffic and providing additional passing opportunities, including:
- Finishing the widening of Highway 17 for 22.5 km from Arnprior to Renfrew to four lanes.
- Widening Highway 6 in Hamilton to double capacity from two to four lanes over a nine-km segment between Highway 403 and Upper James Street.
- Widening Highway 3 from two to four lanes for 15.6 km between the Town of Essex and the Town of Leamington.
Expanding GO Transit
Transit ridership is recovering from the COVID‑19 pandemic, and Ontario is continuing to transform the GO Transit rail network into a modern, reliable and fully integrated rapid transit network. Investing in expanding GO Transit service will generate 8,300 annual job equivalents in the first 12 years of construction and delivery. It will also help reduce commute times and emissions. These investments will improve access and convenience across the Greater Golden Horseshoe and into Southwestern Ontario by steadily increasing service with faster trains, more stations and better connections.
- GO Expansion Development Phase: GO Expansion will bring two-way, all-day GO train service across key parts of the network. The contract to design, build, operate and maintain the GO network, including upgrades to key corridors, has been awarded. The successful proponent has already begun the development phase to finalize the scope, pricing, design and construction schedules. Infrastructure upgrades will include adding tracks, expanding stations, electrification of core parts of the rail network, new locomotives and train control systems to enable more frequent service.
- The Bowmanville GO Rail Extension: The extension of the GO Lakeshore East line to Bowmanville will help relieve gridlock and provide expanded rail service in Durham beyond the current terminus at Oshawa GO Station. Ontario has started the procurement process and the Request for Proposals (RFP) to construct the required rail infrastructure was released in April 2022.
- Expanding the Kitchener Corridor: Ontario is moving forward to deliver two-way, all-day service from Union Station in Toronto to Kitchener. This will provide more trips at every point along the line, improve regional connectivity, support economic development and help reduce congestion. In May 2022, Ontario awarded a key contract for the Guelph Central GO Station to construct a second platform, a new storage track for maintenance vehicles and a passing track in the community of Breslau to allow trains moving in opposite directions to pass each other.
Building Subways

In the 2019 Budget, Ontario announced its historic new vision for transit in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA). Ontario’s bold plan for the largest subway expansion in Canadian history includes the Ontario Line, the Scarborough Subway Extension, the Yonge North Subway Extension and the Eglinton Crosstown West Extension.
The combined subway projects will support more than 16,000 jobs annually during construction over the next decade. Shovels are in the ground with recent milestones including:
- Ontario Line: In September 2022, Ontario announced the preferred proponent teams to deliver two key contracts for the Ontario Line — the South Civil, Stations and Tunnel and the Rolling Stock, Systems, Operations and Maintenance contracts. Both contracts are expected to be awarded later this year. Procurements for the Northern Civil, Stations and Tunnel contract and other enabling works will follow.
- Scarborough Subway Extension: Diggy Scardust, the tunnel boring machine for the Scarborough Subway Extension, is assembled and getting ready to start tunnelling. The Request for Proposals (RFP) for the Stations, Rails and Systems contract closed in July 2022. Teams have submitted their proposals for how they will design and build the stations, lay down the tracks, and install the technology that will connect the extension to the Line 2 subway. A proponent will be selected in fall 2022 to begin the development phase of the project.
- Yonge North Subway Extension: In September 2022, the Yonge North Subway Extension made another stride towards breaking ground with confirmation of a partner chosen to complete upgrades at Finch Station. Construction on the early works, which will include improvements made to the electrical system that powers the rails, is expected to start in the fall of 2022.
- Eglinton Crosstown West Extension: In April 2022, Ontario invited shortlisted bidders to submit formal proposals to design and build the elevated section of the project. Tunnelling on the project has also commenced, with the tunnel boring machines Rexy and Renny leading the charge. As of early October, they had travelled 865m and 1,582m respectively.
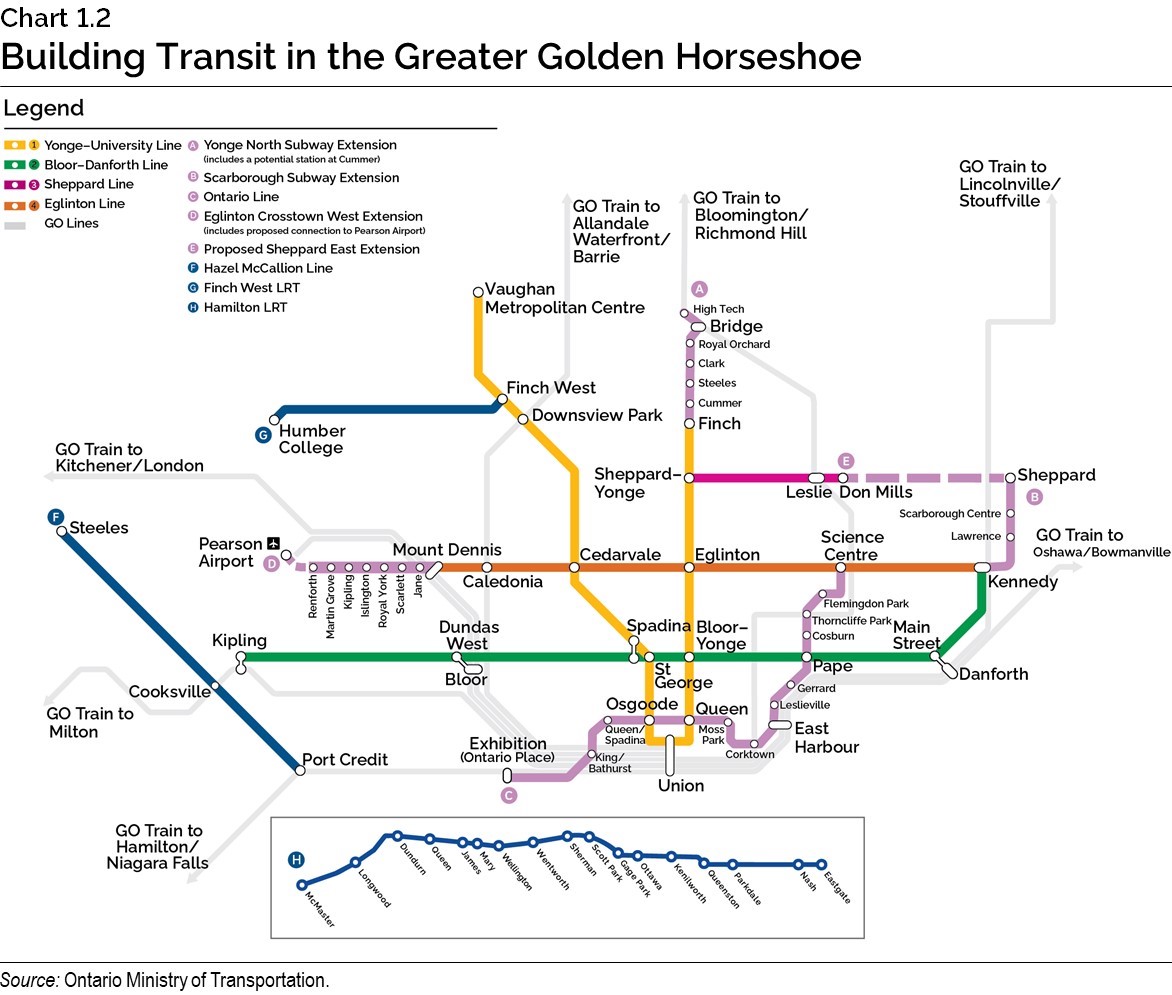
Building Light Rail Transit
The government continues to make progress on delivering rapid transit projects to make life easier for people by reducing travel times and creating more transit options.
- Hazel McCallion Line: The Hazel McCallion Line will bring an environmentally friendly and reliable transportation system to Mississauga and Brampton. In summer 2022, track installation began on Hurontario Street and at the Operations, Maintenance and Storage Facility.
- Finch West Light Rail Transit: The Finch West Light Rail Transit will bring fast, reliable transit from Humber College to Finch West Station. Nearly half of all the track is now installed along the route. The light rail vehicle testing phase is continuing.
- Hamilton Light Rail Transit: Ontario continues to work closely with the City of Hamilton and the federal government to advance the Hamilton Light Rail Transit project. Design and preliminary works are continuing in preparation for construction.
Building Transit-Oriented Communities
Transit-Oriented Communities (TOC) will help increase transit ridership, provide more options for people to live and work near transit, and build more homes, including affordable housing, supporting a growing population. The government is leading the TOC program by leveraging third‑party investments to build vibrant, complete communities within walking distance to GO Transit, light rail transit (LRT) and priority transit lines.
The Ontario government continuously engages with municipalities and building partners to explore new funding avenues and opportunities to deliver transit at a lower cost to taxpayers. Recent examples of engagement include:
- Building partners have been found for several future stations, with the government signing an agreement with Cadillac Fairview in April 2022 for a TOC at the future East Harbour Transit Hub.
- Advancing plans to build a TOC at the future Bridge and High Tech stations in York Region. The TOC at the future Bridge and High Tech Stations along the Yonge North Subway Extension will support a new station at Royal Orchard.
- The government continues to prepare for the selection of building partners for TOC sites at future stations across the new priority subway lines including the Corktown, Queen-Spadina, King‑Bathurst and Exhibition stations.
Building Northeastern Passenger Rail
The government is moving ahead with plans for passenger rail service in the Northeast. In April 2022, Ontario released an updated initial business case to advance planning of the preferred route, moving one step closer to building a more connected transportation network that would support economic opportunities, the tourism industry and improve access to health care, and to education as well as other critical services.Building Community Infrastructure
Building and upgrading community infrastructure is vital to support a growing population and provide dependable services to the people of Ontario. At a time of economic uncertainty, investing in local infrastructure supports jobs and improves vital services including health care and long-term care.
Building and Improving Hospitals and Other Health Care Facilities
As part of its plan to build a stronger, more resilient health care system that increases access to reliable quality care, the government is implementing the most ambitious plan for hospital expansion in Ontario’s history, investing more than $40 billion over the next 10 years to improve and increase space in hospitals and community health centres and build new health care facilities. This includes supporting more than 50 major hospital projects that would add 3,000 new beds over 10 years — projects that build a stronger health care system and create local construction jobs. Recent milestones include:
- Trillium Health Partners Broader Redevelopment – Queensway Health Centre: In October 2022, Ontario released the Request for Proposals (RFP) for the Queensway Health Centre. This critical expansion and redevelopment will include a new nine-storey inpatient tower with over 350 beds, including over 150 new beds. The expansion will also increase capacity for specialized care including complex continuing care and rehabilitation services.
- Trillium Health Partners Broader Redevelopment – Mississauga Hospital: In September 2022, Ontario closed the RFP for the Mississauga Hospital. The new hospital is expected to add over 350 new hospital beds and over 20 new operating rooms to become one of the largest emergency departments in Ontario.
- Weeneebayko Area Health Authority – Health Campus of Care: In August 2022, Ontario closed the RFP for the development phase of the project which includes building a new culturally appropriate hospital with expanded mental health services and an elder care lodge in Moosonee, as well as an ambulatory care centre on Moose Factory Island.
- Niagara Health System – New South Niagara Hospital: RFP submissions are currently being evaluated for the new South Niagara Hospital. The new hospital is planned to have 469 beds and will consolidate and expand acute care services as well as feature several centres of excellence specializing in stroke, complex care and geriatrics.
Additionally, shovels are in the ground on many major hospital projects, including:
- West Lincoln Memorial Hospital Redevelopment Project: In May 2022, Ontario started construction on the new West Lincoln Memorial Hospital, which includes the construction of a new facility with 61 inpatient beds, emergency and ambulatory care departments, surgical services and clinical support services. The project is scheduled to be complete in winter 2025.
- Anishnawbe Health Toronto Indigenous Community Health Centre: Construction is well underway for a new Indigenous Community Health Centre Facility for Anishnawbe Health Toronto. The new four-storey building will consolidate a range of programs from primary care to traditional Indigenous services under one roof to centralize and improve access to health care services. The project is scheduled to be complete in summer 2023.
- Grey Bruce Health Services – Markdale Hospital: Construction of a new state-of-the-art hospital will provide a modern, 24/7 emergency department and larger space to double outpatient care, expand procedural services and increase access to clinical laboratory and diagnostic imaging services. The new facility will improve access to high-quality care for residents in Grey County and is scheduled to be complete in spring 2023.
- The Ottawa Hospital – Stem Cell Program Project: The project involves phased renovations to the existing site to create 12 new inpatient beds, eight new treatment bays in the medical daycare unit, four new hospital day beds and four new exam rooms in the outpatient clinic to upgrade support services and reduce wait times. The final phase of the project is scheduled to be complete in winter 2023.
Building Long-Term Care
Ontario continues to make progress on its plan to build modern, safe and comfortable long-term care homes for seniors and residents. Through planned investments that total a historic $6.4 billion since 2019, Ontario is on track to build more than 31,000 new and over 28,000 upgraded beds across the province by 2028, of which, over 1,900 new and upgraded beds have been completed. Many new long-term care beds will be in homes offering culturally and linguistically appropriate services to better serve Ontario’s seniors.
Of the 364 projects announced to date, 139 projects are proposed to be part of the “campus of care” models which integrate the long-term care home into the broader health care system and ensure residents have access to the care they need. Recognizing the diversity of the province’s aging population, 30 projects are proposed to serve Indigenous communities, and 39 are proposed to serve Ontario’s Francophone population.
Table 1.2
Long-Term Care Projects Highlights
Planning
- Schlegel Villages will build 640 new long-term care beds in Oakville using government surplus lands.
- The Northern Heights Care Community project will build 12 new long-term care beds and upgrade 148 long‑term care beds in North Bay.
- The Golden Manor project will build 15 new long-term care beds and upgrade 177 long-term care beds in Timmins.
- The St. Joseph’s Health Centre Guelph expansion project will build 160 new long-term care beds in Guelph.
Under Construction
- Construction is underway for the Temiskaming Lodge project to build 46 new long-term care beds and upgrade 82 long-term care beds in Temiskaming Shores.
- Construction is underway for the Extendicare Sudbury project to upgrade 256 long-term care beds.
- Construction is underway for the Runnymede Healthcare Centre to build 200 new long-term care beds in Toronto.
- Construction is underway for the Stoneridge Manor project to build 68 new long-term care beds and upgrade 60 long-term care beds in Carleton Place.
- Construction is underway for the Golden Plough Lodge redevelopment project to build 29 new long-term care beds and upgrade 151 long-term care beds in Cobourg.
- Construction is underway for the Ritz Lutheran Villa project to upgrade 128 long-term care beds in Mitchell.
- Construction is underway for the Linhaven Long-Term Care Home project to build 13 new long-term care beds and upgrade 226 long-term care beds in St. Catharines.
- Construction is underway for the Gilmore Lodge project to upgrade 160 long-term care beds in Fort Erie.
- Construction is underway for Maple View Lodge to build 132 new long-term care beds in Athens.
Completed
- Southbridge London opened in August 2022 with 160 upgraded long-term are beds in London.
- Westhills Care Centre opened in May 2022 with 96 new long-term care beds and 64 upgraded long-term care beds in St. Catharines.
- Lakeridge Gardens opened in March 2022 with 320 new long-term care beds in Ajax.
- The Royal Rose Place expansion opened in March 2022 with 64 new long-term care beds in Welland.
- The Villa Care Centre opened in March 2022 with 51 new long-term care beds and 109 upgraded long‑term care beds in Midland.
- The Mon Sheong Stouffville Long-Term Care Centre opened in October 2021 with 320 new long-term care beds in Whitchurch-Stouffville.
- The Grove Nursing Home opened in October 2021 with 36 new long-term care beds and 60 upgraded long-term care beds in Arnprior.
- Elmwood Place opened in September 2021 with 50 new long-term care beds and 78 upgraded long-term care beds in London.
- The Faith Manor project opened in July 2021 with 40 new long-term care beds and 120 upgraded long-term care beds in Brampton.
- Glen Hill Terrace opened in May 2021 with 160 upgraded long-term care beds in Whitby.
- The Algonquin Nursing Home project opened in June 2019 with 72 upgraded long-term care beds in Mattawa.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Long-Term Care.
Building Schools
Ontario is building technologically connected and modern classrooms to support student success. This is why the government is investing $14 billion in capital grants over 10 years to construct more schools and support additions and renovations to existing schools and child care spaces. As part of this investment, $1.4 billion will support the repair and renewal of schools for the 2022–23 school year. The government is also continuing with innovative opportunities to expedite school construction. By investing in the building and renewal of schools, the government is providing healthy learning environments for Ontario students.
To expand child care, Ontario is partnering with the federal government to create 86,000 new, high‑quality, affordable child care spaces by 2026. Of this total, Ontario has already created more than 15,000 new spaces, including over 1,500 new licensed child care spaces in schools.
Table 1.3
Examples of School Projects Underway
Northern
- Construction is underway for a new English public elementary school in North Bay which will serve 308 students and include 73 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary and secondary school in Rainy River will serve 311 students and include 39 licensed child care spaces.
- The H.M. Robbins Public School addition in Sault Ste. Marie will add 26 spaces and will now serve 266 elementary students and include 64 licensed child care spaces.
- A new French public elementary school in Thunder Bay will serve 257 French-language students.
Eastern
- A new English Catholic elementary school in Gloucester will serve 507 students and include 39 licensed child care spaces.
- A new French Catholic elementary school in Kemptville will serve 417 French-language students and include 39 licensed child care spaces.
- Construction is underway for a new English public elementary school in Ottawa which will serve 674 students and include 39 licensed child care spaces.
- Construction is underway for a new English public secondary school in Stittsville which will serve 1,353 students.
Southwestern
- A new English Catholic secondary school in Brantford will serve 1,119 students and include 128 licensed child care spaces.
- The Errol Village Public School addition in Camlachie will add 46 spaces and will now serve 236 elementary students and include 49 licensed child care spaces.
- Construction is underway for a new English public elementary and secondary school in Kingsville which will serve 1,798 students and include 98 licensed child care spaces.
- The Northwood Public School addition in Windsor will add 184 elementary spaces and will now serve 994 students.
Central
- Construction is underway for a new English public elementary school in Brampton which will serve 850 students and include 73 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English Catholic secondary school in Milton will serve 1,611 students.
- Construction is underway for a new English public secondary school in Toronto which will serve 922 students.
- A new French Catholic elementary school in Whitby will serve 354 French-language students and include 49 licensed child care spaces.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Education.
Building Through the Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program
The Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program (ICIP) provides $30 billion in combined federal, provincial and partner funding over 10 years. Since June 2018, Ontario has committed to investing a total of $10.2 billion across five ICIP sub-streams: the Public Transit Infrastructure Stream; Green Infrastructure Stream; Rural and Northern Communities Infrastructure Stream; COVID‑19 Resilience Stream; and the Community, Culture and Recreation Stream. These investments help communities meet the demand for infrastructure renewal, respond to a changing climate and support economic growth.
Table 1.4
Examples of Recently Approved and Completed Projects Under the Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program
Northern
- Approved replacement of 1,145 metres of local drinking water pipes in the Municipality of Red Lake to increase the reliability and capacity of its watermain infrastructure.
- Completion of the replacement of the Black Bridge in the Town of Bracebridge with a single-lane bridge and pedestrian walkway.
Eastern
- Approved upgrades to the Hiawatha First Nation water treatment system to provide residents with a safe and reliable drinking water supply.
- Completed construction of a new youth services facility and community interest centre to serve at-risk communities in the City of Ottawa.
Southwestern
- Completion of the reconstruction of Inglis Fall Road in the Township of Georgian Bluffs to replace deteriorated pavement surfaces and construct retaining walls along the side of the roadway.
- Approved construction of a new elevated water storage facility in the Municipality of Bluewater to maintain efficient operation of the community’s water system.
Central
- Approved upgrades to the chlorine gas system at the water treatment facility in the City of Orillia to increase access to clean and reliable drinking water.
- Completed the rehabilitation of the dam and channel in the Belfountain Conservation Area in the Town of Caledon with a new flood-resilient pedestrian bridge, rehabilitation of the existing boardwalk trail and restoration of culture heritage masonry.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Infrastructure.
Connecting Ontario Through Broadband
Access to high-speed internet allows families and workers to learn, start a business, access vital services like health care, participate in the agricultural sector, and connect with loved ones and friends. The government is investing nearly $4 billion to ensure every community across the province has access to high‐speed internet by the end of 2025. To date, over $950 million has been allocated to nearly 190 high-speed internet, cellular and satellite projects. Additionally, through a new competitive process, the government has signed agreements with eight internet service providers to bring access to up to 266,000 unserved and underserved homes and businesses in as many as 339 municipalities across Ontario.
The government continues to expand access to high-speed internet in Ontario through other initiatives already underway, including:
- Investing more than $109 million in Telesat’s next‐generation, state-of-the art Low Earth Orbit satellite network, to help secure future access to dedicated high‐speed bandwidth for remote communities.
- Investing $71 million in the Eastern Ontario Regional Network (EORN) to improve access to cellular service. This project is expected to generate as many as 3,000 jobs over 10 years and provide greater choice to residents and businesses.
- Investing more than $63 million in the Southwestern Integrated Fibre Technology (SWIFT) project to bring high‐speed internet access to 63,000 more homes, businesses and farms across Southwestern Ontario. To date, over 40 of 97 SWIFT projects have been completed, bringing high-speed internet access to over 30,000 homes and businesses. Construction is underway for the remaining projects and is expected to be complete by 2023.
- Supporting broadband upgrades at approximately 111 libraries with a provincial investment of more than $4.8 million through the Connecting Public Libraries initiative. Through the successful Request for Proposal process, upgrades are possible for over double the original target of 50 public library branches.
- Improving connectivity in Northern Ontario, including $10.9 million to bring improved internet access to several towns and First Nation communities across Northern Ontario.
Redeveloping Ontario Place
The Ontario government is collaborating with the City of Toronto on the redevelopment of Ontario Place. The redevelopment is expected to create more than 5,000 construction and operations jobs and attract approximately five million visitors annually.
- Earlier in fall 2022, repairs to the landmark heritage features at Ontario Place began, including upgrades to a bridge near the marina and preparations to repair the exterior of the Cinesphere.
- Additional work is planned, including repairs to the Pod Complex for late fall 2022.
Keeping Costs Down — Progress Report
Cutting the Cost of Driving
Eliminating Licence Plate Renewal Fees and Stickers

People and businesses continue to feel the pinch of higher costs and the government has taken action to help make life more affordable for nearly eight million vehicle owners in Ontario.
- The government put money back in people's pockets by passing legislation in March 2022 to enable the government to refund eligible licence plate renewal fees paid since March 2020.
- The government also eliminated licence plate renewal fees and plate stickers on a go-forward basis for passenger vehicles, light-duty commercial vehicles, motorcycles and mopeds that are owned by individuals, a company or business which saves vehicle owners $120 a year in Southern Ontario, and $60 a year in Northern Ontario for passenger vehicles and light-duty commercial vehicles.
Removing Tolls on Highways 412 and 418
The government has permanently removed tolls on Highway 412 and Highway 418 to help keep costs down for families and businesses in Durham Region. Highways 412 and 418 were the only tolled north-south highways in Ontario. The removal of these tolls will save the average commuter $7.50 per trip on Highway 418 and $3.74 per trip on Highway 412, as well as relieve gridlock on local roads across Durham Region, and help improve the economic competitiveness of local businesses.
Making It Easier and More Affordable to Take Transit
The government has made it more affordable, easier and more convenient for families and workers to travel across the Greater Golden Horseshoe by eliminating double fares for most local transit when using GO Transit services, increasing PRESTO discounts for youth and postsecondary students and providing more riders with more ways to pay.
- The GO Transit co-fare discounts apply to the following agencies: Durham Region Transit, Milton Transit, Grand River Transit, Guelph Transit, Oakville Transit, MiWay (Mississauga Transit), Brampton Transit, Hamilton Street Railway, Burlington Transit, Bradford West Gwillimbury Transit, York Region Transit and Barrie Transit.
- Local transit is now free for riders connecting to and from GO Transit on municipal transit systems with existing GO Transit co-fare agreements. In addition, PRESTO discounts for youth and postsecondary students almost doubled, increasing to 40 per cent off the full adult fare. Children aged 12 and under continue to travel for free on all GO Transit trains and buses.
- In August 2022, the government created more options to pay for transit, including credit cards on a smartphone or smartwatch, making it easier and more convenient for commuters on the entire GO Transit network, as well as on the Brampton, Mississauga and Oakville transit systems.
- The government is making regional transit more integrated by passing legislation that, when proclaimed, will help to create seamless transit services across the Toronto municipal boundaries. Addressing this long-time barrier to cross-boundary transit services is an important step towards achieving a fully integrated and optimized transit network.
Helping Those Who Need It Most
The impact of rising prices is felt first and hardest by the most vulnerable, including low-income families, workers and seniors. This is why the government continues to keep costs down for those who need the most help.
Helping Lower-Income Workers

Ontario is committed to helping lower-income workers keep more of their hard‐earned money.
- Since the introduction of the Low-income Individuals and Families Tax (LIFT) Credit, more lower‐income workers have paid little or no Ontario Personal Income Tax. Combined with other tax relief, the introduction of the LIFT Credit means that about 90 per cent of all Ontario tax filers with taxable incomes below $30,000 pay no Ontario Personal Income Tax (PIT).
- The government recently enhanced the LIFT Credit. The enhancement increased the maximum benefit from $850 to $875. It also raised the income thresholds and lowered the phase-out rate from 10 per cent to five per cent, increasing and expanding the income ranges over which the benefit is reduced. The enhancement of the credit means that 1.1 million lower-income workers will see an additional $300, on average, in tax relief for 2022. More workers now benefit from the LIFT Credit, bringing the total number of beneficiaries to 1.7 million.
Helping Students Catch Up
The government is enhancing its Plan to Catch Up by providing direct payments to parents through an investment of over $365 million this year. The government has launched Catch Up Payments, offering parents $200 or $250 per child to help offset costs as they support their children to catch up. This funding can be used for supports such as tutoring or learning supplies and equipment. These direct payments will help make life more affordable for parents, and ensure students receive the support they need.
Expanding Energy Efficiency Programs to Help Families and Businesses Keep Costs Down
The government directed the Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) to report back with options for energy efficiency programs that would contribute to meeting electricity system needs.
The government is accepting the IESO recommendations to increase its energy-efficiency programs by $342 million, bringing the total investment to more than $1 billion over the current four-year electricity conservation framework.
The new and expanded programs will help families and businesses reduce electricity use so they can save money on their energy bills, while helping to meet the province’s emerging electricity system needs. The funding will support a new voluntary Residential Demand Response Program to help lower energy use at peak times and lower bills. It will also provide targeted support for greenhouse growers in Southwestern Ontario, in addition to enhancements to existing programs.
By 2025, this expansion of energy-efficiency programs will help deliver enough annual electricity savings to power approximately 130,000 homes every year and reduce system costs by over $650 million, for an estimated net benefit of over $300 million.
The overall savings from this energy efficiency programming will result in an estimated three million tonnes of greenhouse gas emission reductions over its lifetime (2023 to 2050).
Helping Seniors Age in Their Own Homes

The government is committed to helping seniors age in their own homes, surrounded by their loved ones, by providing a range of supports to meet their unique needs and circumstances.
- The government introduced the temporary Ontario Seniors’ Home Safety Tax Credit for 2021 and 2022 to help seniors make their homes safer and more accessible.
- The new Ontario Seniors Care at Home Tax Credit will help low‐ to moderate‐income senior families with a broad range of eligible medical expenses, including many expenses that support aging at home. For 2022, this new Personal Income Tax credit will provide an estimated $110 million in support to about 200,000 low‐ to moderate‐income senior families.
- The government is investing more than $1.5 billion over three years to expand home care, allowing seniors to stay in the homes they love, longer. With this investment and other developments, such as virtual care options, seniors and their families now have more opportunities to receive care at home.
Footnotes
[1] Total business investment includes residential and non-residential structures, machinery and equipment and intellectual property products.
[2]Hyeongsuk Jin, Manon Langevin, André Lebel and Michael Haan. “Factors associated with the completion of apprenticeship training in Canada.” Statistics Canada. Insights on Canadian Society, December 6, 2020.
[3] https://www.canada.ca/en/early-learning-child-care-agreement/agreements-provinces-territories/ontario-canada-wide-2021.html
Chart Descriptions
Chart 1.1: Supporting Ontario Businesses
This bar chart illustrates that Ontario businesses are expected to receive $8.7 billion in support in 2022. This includes combined support from lowering payroll costs ($4,070 million), providing electricity and other price relief ($1,525 million), providing income and property tax relief ($1,455 million), cancelling the cap-and-trade carbon tax ($1,260 million), and providing targeted COVID‑19 measures ($345 million).
Notes: Lowering payroll costs includes, supporting Workplace Safety and Insurance Board (WSIB) premium reductions, the WSIB rebate to safe employers, increasing the Employer Health Tax (EHT) exemption to $1 million starting in 2020 and changes to the minimum wage. Providing electricity and other price relief represents lowering electricity prices through the Comprehensive Electricity Plan; reducing LCBO Wholesale Prices for bars, restaurants and other eligible license holders; and the direct savings to businesses from the cut to the gas tax by 5.7 cents per litre and the fuel tax by 5.3 cents per litre for six months beginning July 1, 2022, before the passthrough of some of the savings to households. Providing income and property tax relief includes reducing Ontario’s small business Corporate Income Tax rate; paralleling the federal accelerated writeoff measures in the federal government’s Fall Economic Statement 2018 and federal Budget 2019; paralleling the federal immediate writeoff for investments of up to $1.5 million; introducing and enhancing the Regional Opportunities Investment Tax Credit; lowering high Business Education Tax (BET) rates and not paralleling the federal tax increase on some small businesses earning passive investment income. Targeted COVID‑19 measures include the Ontario Business Costs Rebate Program; providing a six-month interest and penalty relief period for most provincially administered taxes; the Ontario COVID‑19 Small Business Relief Grant; and re-implementing time-limited off-peak electricity rates from January 18, 2022 to February 7, 2022.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Finance.
Chart 1.2: Building Transit in the Greater Golden Horseshoe
This map shows various transit lines in the Greater Golden Horseshoe highlighting the following:
Yonge-University Line
- Provides two-way subway service from Finch Station to Vaughan Metropolitan Centre Station connecting North York and Vaughan.
- Key stops from east to west include Sheppard Yonge, Eglinton, Bloor-Yonge, Queen, Union Station, St George, Spadina, Cedarvale/Eglinton West, Downsview Park, and Finch West.
Bloor-Danforth Line
- Provides two-way subway service from Kennedy Station to Kipling Station connecting Scarborough to Etobicoke.
- Key stops from east to west include Main, Pape, Bloor-Yonge, St George, Spadina and Dundas West.
Sheppard Line
- Provides two-way subway service from Don Mills Station to Sheppard Yonge Station in North York with a key stop at Leslie Station.
Eglinton Line
- Provides two-way light rail service from Kennedy Station to Mount Dennis Station along Eglinton Avenue.
- Key stops from east to west include Science Centre, Eglinton, Cedarvale, and Caledonia.
GO Lines
- The Barrie Line provides GO train service from Union Station in downtown Toronto to Allandale Waterfront Station in Barrie.
- The Kitchener Line provides GO train service from Union Station in downtown Toronto to Kitchener.
- The Lakeshore East Line provides GO train service from Union Station in downtown Toronto to Oshawa/Bowmanville.
- The Lakeshore West Line provides GO train service from Union Station in downtown Toronto to both Hamilton and Niagara Falls.
- The Milton Line provides GO train service from Union Station in downtown Toronto to Milton.
- The Richmond Hill Line provides GO train service from Union Station in downtown Toronto to Bloomington Station in Richmond Hill.
- The Stouffville Line provides GO train service from Union Station in downtown Toronto to Lincolnville Station in Stouffville.
Yonge North Subway Extension
- Will provide additional two-way subway service north of Finch Station with five new additional stations — Steeles, Clark, Royal Orchard, Bridge and High Tech.
- Potential Station at Cummer.
Scarborough Subway Extension
- Will provide additional two-way subway service northeast of Kennedy Station with three new stations — Lawrence, Scarborough Centre, and Sheppard.
Ontario Line
- Will provide additional two-way subway service connecting the Ontario Science Centre to Exhibition Place through downtown Toronto.
- The new line will feature 15 stops including Flemingdon Park, Thorncliffe Park, Cosburn, Pape, Gerrard, Leslieville, East Harbour, Corktown, Moss Park, Queen, Osgoode, Queen/Spadina and King/Bathurst.
Eglinton Crosstown West Extension
- Will provide additional light rail service west of the future Mount Dennis station with seven new proposed stops at Jane, Scarlett, Royal York, Islington, Kipling, Martin Grove and Renforth.
- Includes proposed connection to the Toronto Pearson International Airport.
Proposed Sheppard East Extension
- Would provide additional two-way subway service by expanding the existing Sheppard Line east of Don Mills Station to the new Sheppard Station in Scarborough.
Hazel McCallion Line
- Will provide new light rail service in Peel Region connecting Port Credit Station in Mississauga to Steeles Station in Brampton along Hurontario Street.
Finch West LRT
- Will provide new light rail service connecting Finch West Station on the Yonge-University Line to Humber College.
Hamilton LRT
- Will provide new light rail service connecting Eastgate Square to McMaster University through downtown Hamilton.
- The new line will feature 17 stops including Nash, Parkdale, Queenston, Kenilworth, Ottawa, Gage Park, Scott Park, Sherman, Wentworth, Wellington, Mary, James, Queen, Dundurn and Longwood.