As Ontario continues its plan to rebuild the economy, the government remains committed to investing in workers and key public services, without raising taxes or fees.
Working for Workers
Ontario is continuing to make it easier for workers to get the skills they need for better jobs and bigger paycheques, while also helping them to plan for a secure retirement. The provincial government is making investments in training to help fill in-demand jobs in key areas like the skilled trades and health care, strengthening Ontario’s economy and helping prepare the skilled workers needed to build roads, transit, hospitals and homes.
Supporting Skills Development and Training
Investing in Skills Training Through the Skills Development Fund Training Stream
The Skills Development Fund Training Stream is helping to address challenges in hiring, training and retaining workers through an additional $100 million in 2024–25 to help workers and job seekers, including apprentices, get the skills they need to advance in their careers. This is in addition to the over $860 million that has been invested since its launch in 2021. To date, the government has delivered close to 600 training projects to help more than 500,000 workers, including those in the skilled trades and health care, take the next step in their careers.
Building New Skilled Trades Training Centres
Ontario is investing $224 million to expand access to bricks-and-mortar training centres through the Skills Development Fund Capital Stream. The funding will help unions, Indigenous centres, and industry associations build new training centres, or upgrade and convert existing facilities into new training centres with state-of-the-art equipment and technology. The investments made through the Skills Development Fund Capital Stream will help ensure that Ontario has the world-class training facilities it needs to train more workers for the skilled trades and build Ontario’s economy. These training centres will prepare people for emerging and in-demand jobs in critical sectors, including construction and health care, among others.
Training Apprentices Through Ontario’s Skilled Trades Strategy
Ontario is helping people explore and prepare for life-long careers in the skilled trades to support the province’s growing economy, deliver on the government’s ambitious capital plan, and support better jobs and bigger paycheques. The government has invested more than $1 billion in the skilled trades through its Skilled Trades Strategy and is providing an additional $16.5 million annually over the next three years to support a variety of programs that focus on breaking the stigma and attracting more young people into the skilled trades, simplifying the system and encouraging employer participation in apprenticeships.
Helping Young People Kick-Start Careers in the Skilled Trades
Ontario is investing over $62.9 million in two of the province’s foundational programs to help more than 18,000 young people explore careers in the skilled trades, including:
- $21.1 million to expand the Ontario Youth Apprenticeship Program (OYAP), a specialized high school program that gives students who have completed Grade 10 the chance to explore the trades through cooperative education courses, while completing their Ontario Secondary School Diploma; and
- $41.8 million to launch approximately 100 pre‑apprenticeship training projects around the province to help young people get firsthand experience working in trades, including a paid work placement with a local employer.
This funding for skills development and training programs will help train the skilled workers needed to build transit, hospitals and at least 1.5 million homes by 2031.

Helping Workers Train for In-Demand Jobs Through Better Jobs Ontario
The Better Jobs Ontario program helps eligible job seekers access short-term training programs by providing up to $28,000 to cover expenses such as tuition, transportation and child care. In the 2023 Budget, Ontario invested an additional $15 million over three years to support the recent expansion of the program to more job seekers including youth, gig workers, newcomers and those on social assistance who may face barriers to finding stable employment. Since January 2021, this program has supported over 7,700 people looking to find better jobs and bigger paycheques.
Helping Workers Plan for Retirement
Implementing a Target Benefit Framework
Target benefit pension plans provide a monthly stream of income in retirement at a predictable cost for employers. Multi-employer pension plans that provide target benefits are often created by a union or association within a specific industry, especially industries involving the skilled trades. This means members of these plans can move from employer to employer while continuing to participate in the same pension plan, which encourages job mobility and will help to attract more people into the skilled trades.
The government has been engaging with the sector over the past year on a permanent target benefit framework that builds on best practices for plan funding and governance and enhances communication with plan members. Taking into consideration feedback received during these consultations, the government is now drafting proposed regulations that would support the framework. These proposed regulations will be made available for technical review by the sector in summer 2024.
The government is also proposing legislative amendments that would support implementation of the framework. The government intends for the permanent target benefit framework to come into effect on January 1, 2025.
The permanent framework would help support the sustainability of these workplace pension plans and pave the way for more employers to offer them, helping workers to save for their retirement.
Keeping Costs Down
At a time when inflation and the Bank of Canada interest rates are high and everyday costs are up, the government is keeping costs down for families. While the economic situation remains challenging, Ontario continues to invest in key public services and lay out a path to a balanced budget without raising taxes or fees. Through investments and relief measures, the government aims to help with keeping costs down and making life more affordable for people. From housing to postsecondary education to transportation, the government is helping keep costs down for essentials for Ontario families while making the province a more affordable and competitive place to live and work.
Putting Money Back in Your Pocket
Recognizing that it is a challenging time for many across the province, the government is making it more affordable to take public transit, drive a car and attend postsecondary school, among other measures to help keep costs down.
Extending the Temporary Gas Tax and Fuel Tax Rate Cuts
In spring 2022, the Ontario government temporarily cut the gasoline tax rate by 5.7 cents per litre and the fuel tax rate by 5.3 cents per litre.
To provide additional relief to people and businesses, the government is proposing to extend these rate cuts so that the rate of tax on gasoline and fuel (diesel) would remain at nine cents per litre until December 31, 2024. This would save Ontario households $320 on average over two and a half years since 2022. The resulting relief is especially important as the federal carbon tax is set to increase on April 1, 2024.
See the Annex: Details of Tax Measures and Other Legislative Initiatives for more information.
Protecting Against Carbon Taxes
The government is committed to protecting people and businesses from the high costs of a new and unexpected provincial carbon pricing program. This is why the government has taken a meaningful step to protect taxpayers’ hard-earned dollars by introducing legislation that would require the provincial government to first ask the people of Ontario, via a referendum, before implementing a new provincial carbon pricing program.
As the government works to protect taxpayers, Ontario continues to call on the federal government to eliminate the federal carbon tax, which has increased inflation and made life less affordable for the people of Ontario.
Expanding Access to the Ontario Electricity Support Program
The government is keeping electricity costs down for about 100,000 additional families by expanding the eligibility for the Ontario Electricity Support Program (OESP). Beginning March 1, 2024, the income eligibility thresholds for the OESP were increased by up to 35 per cent to provide thousands of additional low-income families access to the program and make electricity more affordable. Families can apply for the OESP at any time. The OESP provides an on-bill credit of $35 to $75 per month, depending on household size, to provide support for low-income households when paying their electricity bills. Higher monthly credits of between $52 to $113 are available to customers who are Indigenous, living with Indigenous family members, using electric heating, or using certain electricity-intensive medical devices.
Continuing to Make Postsecondary Education Affordable Through an Extended Tuition Freeze
The government is continuing to provide financial relief for students and families seeking access to affordable postsecondary education. The provincial government is extending the tuition fee freeze for Ontario students in publicly assisted colleges and universities for at least three more years. Institutions will have the flexibility to increase tuition by up to five per cent for out-of-province domestic students. Since the freeze was first introduced after a 10 per cent reduction in tuition fees, students and parents have saved an estimated $1,600 per year, on average, to attend university and an estimated $350 per year, on average, to attend a public college, compared to what they would have paid under the previous policy.
Keeping Transit Costs Down
Ontario is keeping costs down for public transit riders through One Fare, which will save daily riders on participating systems an average of $1,600 each year. Transit riders will only pay once to transfer between transit systems in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA). This is expected to lead to over eight million new rides every year.
One Fare builds on improvements the government made in 2022 and will make cross-boundary travel more affordable and convenient for students, seniors and other commuters.
Banning Road Tolls
Ontario is keeping costs down for drivers by proposing to ban any new tolls on new and existing provincial highways. This ban would also apply to the Don Valley Parkway and the Gardiner Expressway once uploaded to the province. The government already removed tolls on Highways 412 and 418 in April 2022.
Freezing Driver’s Licence Fees
Ontario is also keeping costs down by freezing fees on driver’s licences and Ontario Photo Cards, ensuring that any future increases can only be made through legislation. This would save drivers an estimated $66 million over the next five years compared to a situation where fees would have increased at a historical rate. The people of Ontario have already saved $22 million since the current freeze was put in place by the government in 2019.
Eliminating Licence Plate Renewal Fees and Stickers
The government put money back in people’s pockets in 2022 by refunding eligible licence plate renewal fees paid since March 2020 for nearly eight million vehicle owners in Ontario. The government also eliminated licence plate renewal fees and plate stickers on a go‐forward basis for passenger vehicles, light‐duty commercial vehicles, motorcycles and mopeds that are owned by individuals, a company or business, resulting in savings of $1.1 billion per year for vehicle owners.
Effective April 2019, the government also eliminated the Drive Clean program for passenger vehicles, saving money for Ontario drivers and reducing the regulatory burden on Ontario families.
Making Auto Insurance Work for You
In alignment with previous Budget commitments, the government will move forward with auto insurance reforms that would empower Ontario drivers with more affordable options, improved access to benefits and create a more modern system. Implementation of the proposed changes will be done in a way to help ensure that drivers are able to make informed decisions when choosing insurance coverage options available to them.
Enabling More Consumer Choice
Mandatory auto insurance accident benefit coverage will continue to apply to medical, rehabilitation and attendant care benefits, while all other benefits would become optional. This would provide drivers with an opportunity to lower their premiums by taking advantage of a wider range of coverage options to meet their needs. For example, drivers may already have access to certain benefits through their workplace benefit plans, so they should have the choice to not have to pay for them twice through their auto insurance policies.

The government will be proposing to make auto insurance pay for medical and rehabilitation benefits following an auto accident before extended health care plans do. This would apply to all automobile accidents, regardless of the injury sustained. The proposed change would ensure that auto insurance companies pay for health care costs before extended health care plans and it would also help reduce paperwork and red tape for patients and their health care providers.
Reviewing Health Service Provider Guidelines and Frameworks
The government is committed to ensuring that those injured in auto accidents continue to receive the care they need and that health service providers are compensated appropriately for their services. The government is requesting that the Financial Services Regulatory Authority of Ontario (FSRA) review the Professional Services Guideline and the Attendant Care Hourly Rate Guideline, and consider updating these guidelines based on their findings. The government will consider FSRA’s findings in future reviews of the Statutory Accident Benefits Schedule.
The government is also requesting that FSRA conduct a review of the Health Service Provider Framework and the Health Claims for Auto Insurance (HCAI) system to find administrative and cost efficiencies to contribute to having a more modern and efficient system.
Moving Forward With Product and Services Innovation
In January 2022, the government enabled a Test and Learn Environment allowing FSRA to support the creation of more innovative auto insurance products and services with the goal to improve customer experience and affordability. The government will continue to work with FSRA to identify further opportunities for innovation, competition and cost reductions by proposing to expand the number of items that could be piloted in FSRA’s Test and Learn Environment.
Ensuring Fair Use of Territorial Ratings
The government, in collaboration with FSRA, is working to ensure there is no unfair use of territorial ratings. In January 2024, FSRA launched a pilot in their Test and Learn Environment to modernize Ontario’s territory rating approach to support fairer pricing for auto insurance.
The Territories Test and Learn Environment allows participating auto insurers to propose and evaluate territory rate changes for private passenger vehicles within the GTA over a minimum two-year period. The findings of this pilot may be applied to other regions over time.
Keeping Taxes Low on Beer and Wine
The Ontario government is keeping costs down by stopping the estimated 4.6 per cent increase to the beer basic tax and Liquor Control Board of Ontario (LCBO) mark-up rates that were scheduled for March 1, 2024. This increase would have resulted from rates being indexed to inflation, which the government has consistently waived over the last six years. This latest freeze will be in place for two years, until March 1, 2026.
The government is proposing to eliminate the 6.1 per cent basic tax at on-site winery retail stores and preparing Ontario-based producers to help with the transition to a more open alcohol marketplace.
The government will conduct a targeted review of taxes and fees on beer, wine and alcoholic beverages with the aim of promoting a more competitive marketplace for Ontario-based producers and consumers.

Supporting Individuals and Families
Financial pressures have left many in Ontario, especially those who are more vulnerable, feeling the burden of rising costs on their household budgets. The government understands that it is a challenging time for many across the province, particularly with recent high inflation. This is why the government has acted early to provide relief, taking steps to provide support and deliver on its commitment to make life more affordable.
Actions taken to date, summarized in Chart 1.5, will total $8.4 billion in relief for families and individuals in the 2023–24 fiscal year.
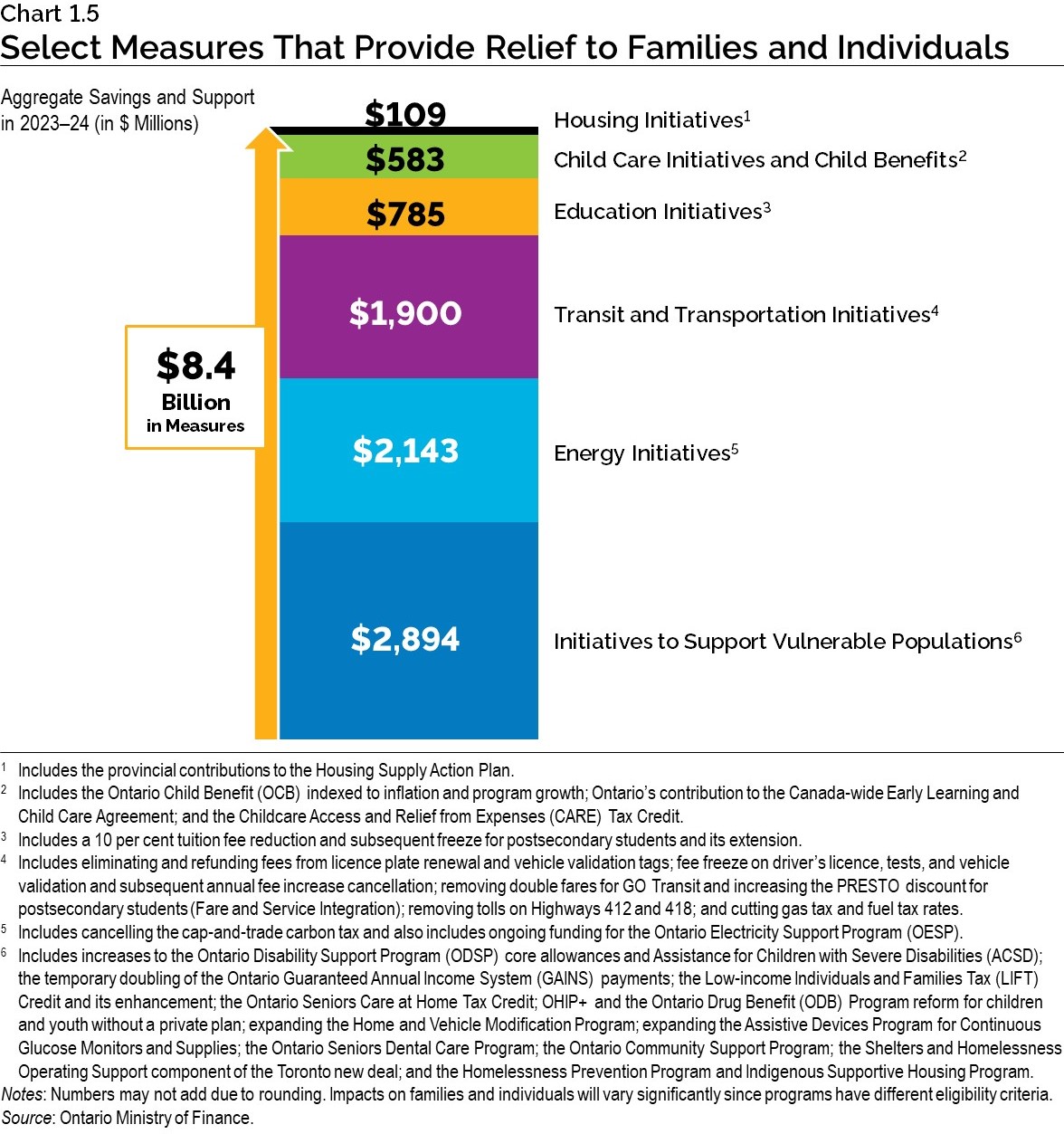
Helping Ontario’s Most Vulnerable
Rising costs have impacted household budgets. The government continues to help Ontario’s most vulnerable, including low-income seniors and individuals living with mental health and addictions challenges who are experiencing unstable housing conditions.
Providing Financial Support to More Seniors
To ensure that more seniors who need financial help get it, the government is expanding the Ontario Guaranteed Annual Income System (GAINS) program and indexing the GAINS benefit to inflation.
Starting in July 2024, the maximum benefit will increase to $87 per month for eligible single seniors and to $174 per month for couples. Going forward, the benefit will be adjusted to inflation annually.
Also in July, the annual private income eligibility threshold will increase from $1,992 to $4,176 for single seniors, and from $3,984 to $8,352 for couples.
These changes will allow about 100,000 more low‐income seniors to receive payments, which is a 50 per cent increase in recipients.

Expanding Access to Supportive Housing
Ontario is investing an additional $152 million over the next three years to support individuals facing unstable housing conditions and dealing with mental health and addictions challenges. This investment aligns with Your Health: A Plan for Connected and Convenient Care and advances the government’s ongoing commitment to expand mental health and addictions support across individuals’ lifespans through Ontario’s Roadmap to Wellness. This funding will go towards a suite of supportive housing initiatives designed to bolster support for vulnerable populations, such as:
- Providing rent supplements for up to 10,679 supportive housing units to mitigate the impact of increasing rent costs due to housing market conditions.
- Maintaining 1,137 dedicated supportive housing units with expiring operating agreements, ensuring continued supportive housing for individuals with mental health and addictions challenges that are at risk of homelessness.
- Providing Indwell Community Homes funding for rent supplements and mental health and addictions support services to maintain supportive housing for over 640 individuals.
- Maintaining supportive housing for Salus in Ottawa and the Canadian Mental Health Association in North Bay and District, through investments to repair and renovate buildings, as well as to relocate up to 79 displaced low-income tenants with mental health and/or addictions needs.
The government will be considering new projects, starting next fiscal year, to build more supportive housing units across the province.
These measures complement the $202 million in additional funding each year for the Homelessness Prevention Program and Indigenous Supportive Housing Program that was announced in the 2023 Budget.
Helping to Increase Housing Supply and Affordability
One way to improve access to the housing market and affordability is to increase housing supply. This is why the government is taking action to make more homes available to the people of Ontario and supporting lower taxes on new purpose-built rental housing.
Empowering Municipalities to Make More Vacant Homes Available for Housing
Ontario will empower municipalities to increase housing supply and address housing affordability through municipal Vacant Home Taxes.
An unoccupied home is unacceptable in a housing crisis, which is why Ontario is extending authority broadly to all single- and upper-tier municipalities to impose a tax on vacant homes. This measure will increase housing supply, address housing affordability, and ensure more Ontario families can afford a home. Currently, Toronto, Ottawa and Hamilton have the authority to impose vacant home taxes.
Municipalities will be supported with a new provincial policy framework that sets out best practices for implementing a Vacant Home Tax. The framework will also encourage municipalities to set a higher Vacant Home Tax rate for foreign-owned vacant homes.
Prioritizing Ontario Homebuyers
Ontario’s Non-Resident Speculation Tax (NRST) is a tax applied at the time of a home purchase by a foreign entity.
The government has taken steps to enhance the NRST — the most comprehensive tax of its kind in Canada — to tackle the issue of foreign investors speculating on the province’s housing market, in order to help make more homes available for the people of Ontario. In 2022, the government expanded the tax provincewide and increased the rate from 15 per cent to 25 per cent. Moving forward, the government is taking further action to strengthen the NRST with amendments to support compliance and improve fairness.
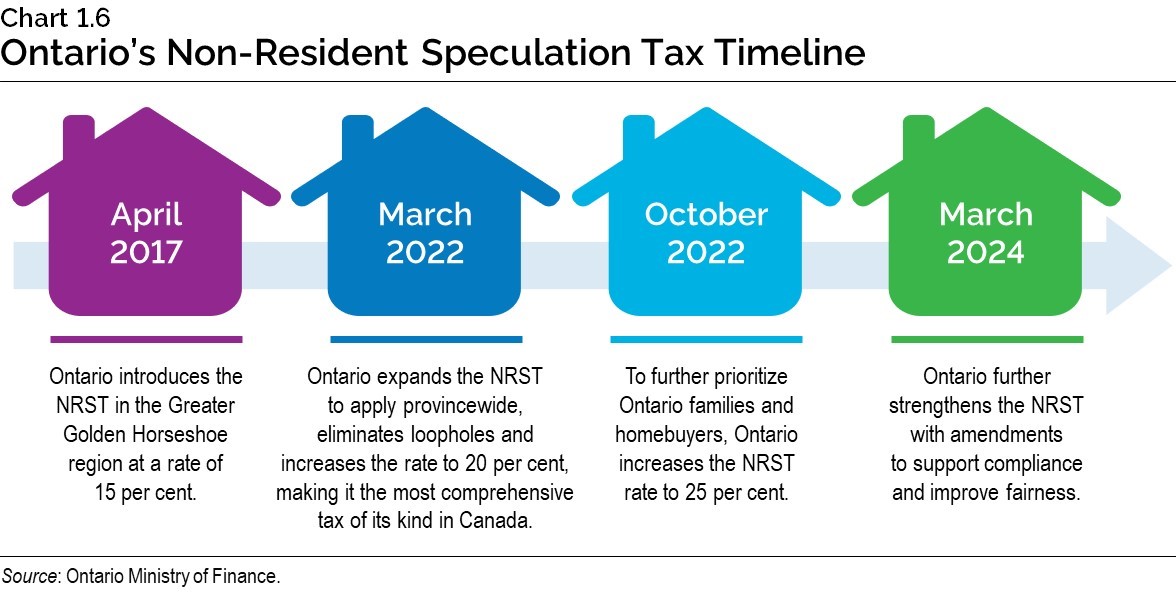
In addition, the government is taking steps to increase information sharing between provincial, federal and municipal governments. Ontario’s leadership on this initiative would support greater understanding of home vacancy, foreign purchasing and ownership patterns. All three levels of government need to work together to solve the housing supply crisis, to ensure Ontario families and homebuyers take priority in the housing market. Data is a powerful tool to better understand vacancy and foreign-purchasing patterns, while simultaneously supporting tax compliance and incentives to discourage speculation.
Removing Harmonized Sales Tax on Purpose-Built Rentals
As announced in fall 2023, Ontario has taken steps to enhance the Ontario Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) New Residential Rental Property Rebate to remove the full eight per cent provincial portion of the HST on qualifying new purpose-built rental housing. This will help encourage the construction of more purpose-built rental housing. Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) data show that 2023 had a record high number of rental housing starts in Ontario. 1
The enhanced relief would apply to new purpose-built rental housing, such as apartment buildings, student housing and senior residences built specifically for long-term rental accommodation. This would mirror the enhancements to the federal Goods and Services Tax/Harmonized Sales Tax (GST/HST) New Residential Rental Property Rebate and together would remove the full 13 per cent HST on qualifying new purpose-built rental housing in Ontario.
The enhanced rebate would apply to qualifying projects that begin construction on or after September 14, 2023, and on or before December 31, 2030, and complete construction by December 31, 2035.
Changes to Ontario’s rebate require federal regulatory changes. Ontario will continue to work closely with the federal government to ensure the coordinated and timely implementation of the enhanced rebate, and to maximize its impact.
Enabling Municipalities to Lower Taxes on New Purpose-Built Rentals
Ontario is committed to addressing the current housing crisis and increasing housing affordability for the people of Ontario. To further encourage the development of purpose-built rental properties, effective immediately, Ontario is providing municipalities with the flexibility to offer a reduced municipal property tax rate on new multi-residential rental properties.
Investing in Innovative Modular Construction
The government recognizes that fresh approaches to tackle Ontario’s housing crisis will give people more options to access housing that is affordable and attainable. As part of this strategy, the government is developing an attainable housing program that will help make homeownership a reality for more Ontario families.
This includes embracing modular construction and other innovative options to accelerate development, improve affordability and nurture home-grown industries that support quality jobs in Ontario. Modular construction involves building a home using one or more prefabricated components or modules. The home is constructed partially or completely off‐site, then transported to a property for assembly.
The government is engaging with the construction sector, municipalities and Indigenous communities on the use of modular construction and other innovative technologies so that more people can live in a home that they can afford. Embracing innovative solutions like modular housing will help improve the supply of affordable and attainable housing for the people of Ontario.
Better Services for You
From health care to child care, transit and justice services, the public services that the people of Ontario need should be convenient and easy to access. The government is challenging the status quo to provide better services for people and businesses across the province.
Making Health Care More Connected and Convenient
The government is continuing to make health care more connected and convenient across the province to ensure patients are provided with the right care in the right place, and have faster access through an expanded health care workforce and enhanced services. This is why, in February 2023, the government introduced Your Health: A Plan for Connected and Convenient Care, which puts people at its heart, by adding and expanding health care services closer to home. The plan is built on three pillars: The Right Care in the Right Place, Faster Access to Care, and Hiring More Health Care Workers.
The government also continues to invest in improved access to digital services for the people of Ontario. This includes enhancing Health811 services to enable increased access to virtual care, online appointment booking, and integration with Ontario Health Teams. This also includes continuing to invest in remote care management, which is integral to supporting patients in the comfort of their homes rather than in hospital for a wide range of conditions, including post-surgical discharge and chronic disease management.
Supporting Home and Community Care
In the 2023 Budget, the government accelerated the commitment of $1 billion over three years to stabilize the home and community care workforce and to support the expansion of home care services. In this Budget, the government is investing an additional $2 billion over three years to boost this acceleration, support earlier investments to increase compensation for personal support workers, nurses and other frontline care providers, and to stabilize expanded services.
The government continues to invest in transforming the home care system, including new models of care and modernizing the Client Health and Related Information System (CHRIS), the digital infrastructure system supporting home care.
For community care, the government is providing supports for the workforce to strengthen adult day programs, meal services, transportation and assisted living services. Having strong home and community care is a key part of the government’s plan for connected and convenient care, to keep people healthy and in the comfort of their homes.
Investing in Hospitals
Ontario recognizes the indispensable role hospitals play in delivering critical health services to communities across the province. This is why the government is investing an additional $965 million in 2024–25, including a four per cent increase in total base hospital funding for an unprecedented second year in a row, to ensure public hospitals are able to meet patients’ needs and to increase access to high‐quality care. This investment also includes funding for stabilization and management of the surgical system, with a focus on maximizing capacity to increase the number of surgeries performed to provide the people of Ontario the care they need with shorter wait times.
As part of ongoing efforts to build a strong and resilient health system, the government is also providing funding to ease pressures faced by small and Northern hospitals. This will help address health human resources shortages, increased agency staffing costs, emergency department closures and other areas requiring stabilization.
These investments demonstrate Ontario’s ongoing commitment to build a more connected and convenient health care system, prepared to face the challenges of today and tomorrow.
Connecting More People to Primary Care
While hospitals are core to Ontario’s health care system, it can be more cost effective and convenient for people to receive care through their family doctors or primary care teams. This is why the government is making historic investments to enhance access to primary care with a goal that everyone who wants to have a primary care provider can connect to one. On February 1, 2024, Ontario announced an investment of $110 million in 2024–25. Building on this, the government will provide a total investment of $546 million over three years, starting in 2024–25. This funding will support connecting approximately 600,000 people to team-based primary care through new and expanded interprofessional care teams. This builds on the 2023 Budget commitment of an additional $60 million in funding, bringing the total investment to $606 million since 2023–24.
Interprofessional primary care teams connect people to a range of health professionals who work together, including doctors, nurse practitioners, registered and practical nurses, physiotherapists, social workers and dietitians, among others. Interprofessional primary care teams enhance the quality of patient care, improve health outcomes, and increase the efficiency of health service delivery by relieving pressures on emergency departments and walk-in clinics.
This investment will also provide support to all existing interprofessional primary care teams through ongoing operational funding for their facilities and supplies so that they continue to provide high-quality care to the people of Ontario. This will further ensure that interprofessional primary care teams can maintain effective direct service delivery to patients.
Funding for new and expanded teams will focus on high-need areas, bringing the government one step closer to connecting everyone in Ontario to primary care. Examples include:
- Peterborough: More than $3 million in funding will allow the newly established Peterborough Community Health Centre to connect up to 11,375 people to team-based primary care.
- Kingston: More than $4 million in funding will help up to 10,000 people connect to team-based primary care at the Periwinkle site.
- North Dumfries: More than $1.9 million in funding to help up to 5,400 people connect to team-based primary care in a rural setting.
- Simcoe Muskoka, Barrie and Orillia: More than $1.4 million to increase access to team-based primary care and mobile services for up to 1,200 people with a focus on Indigenous populations.
- Niagara Region: More than $2.1 million to increase access to team-based primary care across the communities of Fort Erie, Port Colborne, Welland, Niagara Falls and St. Catharines.
- Sault Ste. Marie and Area: More than $1.1 million to two organizations, Maamwesying North Shore Community Health Services Inc. and the Sault Community Health Centre, to help connect people to team-based primary care in Sault Ste. Marie and surrounding First Nation communities.

Strengthening the Health Care Workforce
Ontario is investing $743 million over three years to continue to address immediate health care staffing needs, as well as to grow the workforce for years to come. This includes:
- Making the Extern Program Permanent: This program will offer up to 5,590 health care students training opportunities to work in hospitals and gain practical experience as they continue their education. Since 2021, over 7,300 health care students have participated in the program — creating much needed capacity in the system and a pool of new graduates who are more experienced and prepared to work as they begin their health care careers.
- Making the Supervised Practice Experience Partnership Program Permanent: This program will support up to 1,500 internationally educated nurses annually to become accredited nurses in Ontario. More than 3,600 nurses have participated in this program since its inception and over 2,700 internationally trained nurses are already fully registered and practising in Ontario.
- Increasing Nursing Enrolment: Ontario continues to expand nursing enrolment in colleges and universities to help address the need for nurses now and in the years to come. This is why Ontario is investing an additional $128 million over the next three years to support the sustained enrolment increases of nursing spaces at publicly assisted colleges and universities by 2,000 registered nurse and 1,000 registered practical nurse seats. This expansion is part of the government’s plan to address health human resource needs and support the growing demand for health care professionals in Ontario.
- Merging the Clinical Scholar Program: This program amalgamates the Late Career Nurse Initiative and the Clinical Preceptor Program that support experienced nurses to mentor and coach new graduates and internationally educated nurses, as well as nurses seeking to upskill.
- Upskilling Nurses: This program supports the upskilling of nursing students to be able to work in priority areas within a hospital, such as critical care.
- Stabilizing Emergency Department Staffing: This strategy provides critical investments to bolster and stabilize the emergency department nursing workforce.
Expanding Access to Allied Health Professions
Ontario is continuing to make significant investments to expand access to allied health care providers across the province, including by adding an additional 700 education seats for medical radiation and imaging technologists, medical laboratory technologists, medical lab technicians and medical radiation extenders. Ontario is also working with colleges to explore and pilot compressed programs for pharmacy technicians and medical radiation technologists so more qualified professionals can enter the workforce sooner.
Supporting Northern and Rural Health Care
The government is investing $50 million over three years to enhance and stabilize health care capacity within Northern and rural communities. This investment will introduce long-term solutions encompassing education, recruitment, retention, scope of practice and care models to provide residents of Northern Ontario and those in remote areas with improved access to health care services. This funding will also support the expansion of existing rural generalist pathways for physicians and fund additional supports and upskilling for other health care workers.
The Northern and rural hospitals have exhibited remarkable resilience in the face of health system challenges, with these challenges disproportionately impacting patients who must travel extensive distances for medical care. In recognition of the critical role these hospitals play and to support the communities they serve, the government is expanding services to help prevent emergency department shutdowns.
Adding More Health Care Workers in Underserved Communities
The government remains committed to building a stronger, more resilient health care workforce in underserved communities in Northern, Eastern and Southwestern Ontario through the expanded Ontario Learn and Stay Grant. The grant provides full, upfront funding for tuition, books and other direct educational costs for students who enrol in an eligible nursing, paramedic or medical laboratory technologist program in return for working in the communities where they studied for a term of service after graduation.
Supported by over $30 million in funding to date, there are currently about 3,800 students participating in the program across Ontario. In fact, thanks to the Ontario Learn and Stay Grant, there has been notable uptake in paramedic programs, with almost 40 per cent more students enrolling through the grant in 2023–24 than the previous year’s enrolment in these programs.
Through this initiative, the government aims to deliver more connected health care across Ontario by addressing the increasing demand for nurses, paramedics and medical laboratory technologists while also responding to labour market needs in underserved communities.
Investing in Indigenous and Northern Community Supports
The government is committed to enhancing the health and well-being of Indigenous and Northern communities through several investments totalling approximately $94 million over three years. These investments focus on culturally responsive and safe care tailored to the needs of these communities, such as public health, chronic disease prevention and maternal care, including:
- $60 million over three years to maintain mental health and addictions services, including clinical supports, community mental health and well-being initiatives, and opioid programming.
- $15 million over three years to support the ongoing delivery of Indigenous public health programs, including vaccination initiatives to improve health outcomes.
- $11 million over three years to enhance early detection and management of foot complications arising from diabetes for Indigenous communities. Through prevention and earlier detection, this program aims to improve health outcomes for those living with diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- $8 million over three years to strengthen prevention initiatives in Indigenous communities, targeting diabetes, smoking and chronic diseases.
Supporting Women’s and Children’s Health
The government is taking action to ensure women and children are better able to access culturally responsive and safe care to strengthen the health of their families with investments of $50 million over three years, including:
- $24 million over three years to enhance access to the Indigenous Healthy Babies Healthy Children Program across 160 Indigenous delivery sites. The Indigenous Healthy Babies Healthy Children Program is a community-based initiative aimed at helping Indigenous families and children have a healthy start to life and laying a solid foundation for their future health, well‑being and success.
- $15 million over three years for Mobile Maternal Care. This innovative mobile clinic will offer a range of services, from prenatal to postnatal care, improving accessibility of maternal and newborn health care in remote communities.
- $11 million over three years to support safer births in Northern Ontario. This funding is aimed at improving maternal and newborn health outcomes by providing mothers in Northern Indigenous communities with vital birthing supports, including more doulas, second attendants or birth helpers.
Connecting People to Mental Health Services
Building on the historic investment of $3.8 billion over 10 years for mental health and addictions services as part of the Roadmap to Wellness: A Plan to Build Ontario’s Mental Health and Addictions System strategy, the government is investing an additional $396 million over three years. These investments support the stabilization, improved access and expansion of existing mental health and addictions services and programs.
As part of this investment, the government is providing $124 million over three years to support the continuation of the Addictions Recovery Fund to ensure the people of Ontario continue to have access to enhanced specialized services for mental health and addictions treatment, including:
- Maintaining 383 addictions treatment beds for adults who need intensive supports, helping to stabilize and provide care for approximately 7,000 clients each year;
- Three Mobile Mental Health Clinics to provide a suite of mental health and addictions services to individuals living in remote, rural and underserved communities; and
- Three police-partnered Mobile Crisis Response Teams to support individuals in a mental health or addictions crisis.
The government is also providing ongoing support for the innovative Ontario Structured Psychotherapy Program to support those with anxiety and depression through cognitive behavioural therapy, providing the people of Ontario with high-quality mental health care no matter where they live in the province.
With these investments, the government is continuing to deliver on the Roadmap to Wellness: A Plan to Build Ontario’s Mental Health and Addictions System, connecting those in need of mental health and addictions services to care.
Building and Expanding Hospitals to Improve Care
The government is building a convenient and connected health care system that puts people first. This is why Ontario is delivering on the most ambitious plan for hospital expansion in the province’s history. Ontario’s plan will lead to investments of nearly $50 billion over the next 10 years in health infrastructure, including close to $36 billion in capital grants. This includes supporting more than 50 hospital projects that would add approximately 3,000 new beds over 10 years to improve access to reliable quality care. Recent milestones include:
- Grand River Hospital — MRI Expansion and Upgrade Project: In October 2023, completed renovations and expansion of the MRI, nuclear medicine and imaging spaces to improve patient flow, safety and operational efficiency.
- Health Access Thorncliffe Park — Thorncliffe Park Community Hub Project: In October 2023, awarded the construction contract for the Thorncliffe Park Community Hub. This project will convert approximately 68,000 square feet at the East York Town Centre to an integrated and sustainable multi-service hub that offers primary health care, mental health services, maternal reproductive health care, and newborn, child and youth services. The project is targeted to be completed by August 2024.
- Queensway Carleton Hospital — Phase 3B Mental Health Redevelopment: In November 2023, completed renovations to increase acute mental health beds (to a total of 26 beds) and expand and improve space for inpatient and outpatient mental health programs.
- Quinte Health — Prince Edward County Memorial Hospital Redevelopment Project: In October 2023, moved forward to tender the redevelopment of the Prince Edward County Memorial Hospital with the addition of eight new beds, a 24/7 emergency department, diagnostic imaging and surgical suites, and ambulatory care.
- Sault Area Hospital — Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Project: Opened in January 2024, the new program supports cardiac procedures in Sault Ste. Marie and Northern Ontario.
- The Ottawa Hospital — Civic Campus Redevelopment Project: In February 2024, signed a Development Agreement with The Ottawa Hospital Build Partners. Upon completion, the 641‑bed hospital will have one of the most advanced trauma centres in Eastern Ontario to provide highly specialized emergency and trauma services to treat complex injuries and illness for patients.
- University Health Network — Toronto Western Hospital New Patient Care Tower: In January 2024, awarded the construction contract to build a new 15-storey tower at the Toronto Western Hospital site in downtown Toronto. The project would add 82 new acute care patient beds, 20 state-of-the-art operating rooms, new pre-operative and post-anaesthetic care units and a new pharmacy. The project is targeted to be completed by December 2027.
- West Park Healthcare Centre Redevelopment Project: In November 2023, substantially completed the construction of the new six-storey facility, which will provide increased capacity for inpatient care with up to 314 beds upon opening, as well as outpatient care and diagnostic and therapeutic services.
- Waypoint Centre for Mental Health Care — Additional Acute Mental Health Inpatient Beds Project: In December 2023, announced the project to renovate over 10,000 square feet of existing space to add 20 additional acute mental health beds to the facility. Once complete, the new acute mental health inpatient unit will connect more people and their families to a range of services, including psychiatry, psychology, occupational and recreation therapy, and addictions counselling.
- New Windsor-Essex Regional Hospital: The project will support a new state‐of‐the‐art acute care hospital in Windsor and Essex County to add more hospital beds and expand services in the region with procurement expected to begin in 2025.
Investing in Small Hospitals and Community Infrastructure
In addition to building hospitals, the government is committing an additional $620 million over 10 years for the Health Infrastructure Renewal Fund and the Community Infrastructure Renewal Fund. This funding will allow health care system partners to address urgent infrastructure renewal needs such as upgrades or replacements of roofs, windows, security systems, fire alarms and back-up generators. These investments will ensure funds are available for much-needed equipment upgrades, building repairs, and to extend the life of hospital and community infrastructure.
The government is also committing an additional $500 million over 10 years for small hospital projects and community health programs. These smaller hospital and community projects can create much needed capacity in the short term. Community health programs also help to prevent hospital visits that put pressure on emergency departments as well as hospital admissions.
Building Long-Term Care Homes
Ontario continues to make progress on its plan to build modern, safe and comfortable long-term care homes for seniors and residents. Through planned investments that total a historic $6.4 billion since 2019, Ontario is making progress to build 58,000 new and upgraded beds across the province by 2028.
Increasing the Construction Funding Subsidy
The government is investing $155 million in 2024–25 to increase the construction funding subsidy, to support the cost of developing or redeveloping a long-term care home. This additional investment will fast-track construction for the next tranche of beds so that work can begin by November 30, 2024. Eligible projects will receive an additional construction funding subsidy of up to $35 per bed, per day, for 25 years. In addition, eligible not-for-profit applicants will be able to convert up to $15 per bed, per day, of the supplemental funding into a construction grant payable at the start of construction, to increase projects’ upfront equity and enable applicants to secure financing.
The government first provided a supplemental increase to the construction funding subsidy in November 2022 to stimulate the start of construction for long-term care homes across Ontario. Since introducing the supplemental increase, Ontario advanced construction for over 60 long-term care homes and over 10,000 beds between April 1, 2022, and August 31, 2023.
Making Progress to Build Long-Term Care Homes
Through the Accelerated Build Pilot Program, four new long-term care homes have been built on hospital-owned lands. These homes have created 1,272 new long-term care beds and are helping to meet urgent needs for more long-term care homes in Mississauga, Ajax and Toronto.
The government continues to make progress towards its commitment of building 58,000 new and upgraded beds to modern design standards across the province by 2028 with over 18,000 beds that are either open, under construction, or have approval to start construction. This includes:
- Over 4,500 beds open with new capacity of 2,246 beds and 2,336 upgraded beds;
- Over 12,500 beds under construction with 6,745 new beds and 5,789 upgraded beds; and
- Approximately 1,200 beds that have governmental approvals to start construction.
In response to higher costs in the sector, the government is increasing operating funding to help support the financial stability of new and existing long-term care homes.
The Loan Guarantee Program also continues to be available to support financing of the development of long-term care beds in non-municipal, not-for-profit projects.
Since the 2023 Ontario Economic Outlook and Fiscal Review, the following long-term care homes have been completed and opened to new residents:
- Wellbrook East and Wellbrook West, two new state-of-the-art long-term care homes, opened in November 2023, with 632 new long-term care beds in Mississauga, developed under the Ontario Accelerated Build Pilot Program; and
- Woodland Villa opened in December 2023 with 17 new long-term care beds and 111 upgraded long-term care beds in Long Sault.
Getting Back to Basics in Education
Ontario is supporting a back to basics learning strategy by building foundational skills in reading, writing and math. Students have benefited from a new math curriculum focused on financial literacy and coding, as well as the overhauled language curriculum that brings back phonics and cursive writing. Recent Education Quality and Accountability Office (EQAO) assessment results show encouraging progress, which demonstrates the importance of students learning in the classroom without disruption and with targeted supports focused on literacy and math.
The government will continue existing supports through the back to basics learning strategy, including:
- An investment of $15 million for the 2024–25 school year for digital math tools that will continue to provide anytime access to learning opportunities at home and in the classroom, as part of total funding of about $72 million in math supports. As part of these math supports, the government also continues to support one-on-one French-language online tutoring through Eurêka!;
- An investment of $65 million for the 2024–25 school year for dedicated educators working in small groups or individually with students in kindergarten to Grade 3. This brings total funding to about $100 million for reading supports for the 2024–25 school year; and
- An updated kindergarten curriculum, starting in September 2025, which will introduce learning through clear and direct instruction in reading, writing and math for kindergarten students. Combined with hands-on and play-based learning, the changes will help ensure students entering Grade 1 have the foundational skills needed for long-term success.
Supporting Students with Special Education Needs

Ontario is committed to providing all students with the opportunity to succeed in school and life, including students with disabilities and special education needs. This is why the government is investing $18 million in the 2024–25 school year to help the most vulnerable students.
This includes $8 million to introduce dedicated resources to help students with special education needs navigate the school system and beyond, as well as $10 million for increased in-class supports for students with the highest level of need.
Building Schools and Child Care Spaces
The government is committed to building modern schools by investing $23 billion, including approximately $16 billion in capital grants over 10 years, to build, expand and renew schools and child care spaces across Ontario. Since 2018, the government has supported nearly 300 school or child care-related projects, of which more than 100 are actively under construction. This includes $1.4 billion for the current school year to support the repair and renewal needs of schools.
Table 1.3
School Projects Opening in the 2023–24 School Year
Northern
- Maple View Public School in North Bay, which serves 308 students and includes 73 licensed child care spaces.
- Lasalle Elementary School in Sudbury, which serves 387 students and includes 49 licensed child care spaces.
- École élémentaire publique de Thunder Bay in Thunder Bay, which serves 257 French-language students.
Eastern
- École élémentaire catholique des Deux-Rivières in Arnprior, which serves 248 French-language students and includes 49 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to Westminster Public School in Brockville with 25 more licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to St. Joseph Catholic Elementary School in Douro-Dummer with 92 more student spaces.
- École secondaire publique Mille-Îles and École secondaire catholique Sainte-Marie-Rivier joint school in Kingston, which serves 600 French-language students and includes 49 licensed child care spaces.
- St. Bernadette Catholic Elementary School in Stittsville, which serves 507 students and includes 39 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to Williamstown Public School in Williamstown with 121 more student spaces.
Southwestern
- An addition to Peace Bridge Public School in Fort Erie with 230 more student spaces.
- An addition to St. Anthony’s Catholic School in Kincardine with 190 more student spaces and 78 more licensed child care spaces.
- St. Josephine Bakhita Catholic Elementary School in Kitchener, which serves 650 students and includes 88 licensed child care spaces.
- West Niagara Secondary School in Lincoln, which serves 1,533 students.
- An addition to Hyland Heights Elementary School in Shelburne with 92 more student spaces.
- An addition to Sacred Heart Catholic School in Port Lambton with 46 more student spaces and 49 more licensed child care spaces.
- Eastview Horizon Public School in Windsor, which serves 501 students and includes 73 licensed child care spaces.
Central
- An addition to École secondaire Jeunes sans frontières in Brampton with 207 more French-language student spaces.
- E.J. Sand Public School in Markham, which serves 409 students and includes 39 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to St. Anne Catholic School in Oshawa, with 184 more elementary student spaces.
- Glen Orchard Public School retrofit in Port Carling, which includes 54 licensed child care spaces.
- École secondaire Michelle-O’Bonsawin retrofit in Toronto, which serves 501 French-language students.
- An addition to Terry Fox Public School in Toronto, with 276 more student spaces and 88 more licensed child care spaces.
- Regina Mundi Catholic School retrofit in Toronto, which serves 450 students and includes 88 child care spaces.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Education.
Table 1.4
Continuing to Get Shovels in the Ground to Build More Schools
Northern
- A new joint French and English public elementary and secondary school in Blind River, which will serve 72 French-language students, 381 English language students and include 64 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary and secondary school in Rainy River, which will serve 311 students and include 39 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to Tarentorus Public School in Sault Ste. Marie, which will add 92 student spaces and 49 licensed child care spaces.
Eastern
- A new French public elementary school in Barrhaven, which will serve 475 students and include 49 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to St. Joseph Catholic School in Belleville, which will add 334 student spaces and 49 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary school in Brockville, which will serve 500 students and include 64 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English Catholic School in Kingston, which will serve 481 students and include 73 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to Collège catholique Mer Bleue in Orleans, which will add 343 student spaces.
- A new English public secondary school in Ottawa, which will serve 1,516 students and include 39 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public secondary school in Ottawa, which will serve 1,353 students.
- A new French public school in Ottawa, which will serve 475 students and include 49 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to École secondaire catholique Paul-Desmarais in Stittsville, which will add 389 student spaces.
Southwestern
- A new English public elementary and secondary school in Kingsville, which will serve 1,798 students and include 98 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English Catholic elementary school in Kitchener, which will serve 527 students and include 88 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to St. Louis Catholic Elementary School in Leamington, which will add 147 student spaces and 63 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to Listowel Eastdale Public School in Listowel, which will add 98 student spaces and 49 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary school in London, which will serve 804 students and include 88 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English Catholic elementary school in Sarnia, which will serve 659 students and include 88 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English Catholic elementary school in Stoney Creek, which will serve 590 students and include 49 licensed child care spaces.
- An addition to St. Anne’s School in St. Thomas, which will add 210 Catholic student spaces.
- A new English public elementary school in Windsor, which will serve 651 students and include 73 licensed child care spaces.
Central
- A new English public elementary school in Brampton, which will serve 850 students and include 73 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary school in East Gwillimbury, which will serve 638 students and include 39 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary school in Bowmanville, which will serve 786 students and include 73 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary school in Beaverton, which will serve 418 students and include 49 licensed child care spaces.
- A new Catholic elementary school in Milton, which will serve 671 students and include 88 licensed child care spaces.
- A new English public elementary school in Oro-Medonte, which will serve 570 students.
- An addition to École élémentaire catholique Saint-Michel in Scarborough, which will add 92 student spaces.
- A new Catholic secondary school in Toronto, which will serve 1,300 students.
- A new English public secondary school in Toronto, which will serve 922 students.
- A new French Catholic secondary school in Vaughan, which will serve 407 students and include 49 licensed child care spaces.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Education.
Supporting Efficiency, Transparency and Accountability in the Postsecondary Education Sector
The provincial government is helping to stabilize Ontario’s colleges and universities, with nearly $1.3 billion in new funding, while maintaining the tuition fee freeze to keep costs down for Ontario students and parents. Ontario is focused on supporting the postsecondary education sector in delivering high-quality educational experiences in an efficient, accountable and transparent manner. To help achieve this, Ontario will provide $15 million over the next three years to implement an Efficiency and Accountability Fund.
This fund will support third-party reviews to identify actions that institutions can take to drive long-term cost savings and positive outcomes for students and communities. These reviews will target structural issues as well as operational policies in order to improve sustainability and student experiences. This Efficiency and Accountability Fund is part of Ontario’s plan to help build a financially viable postsecondary sector that supports student success.
Ontario is also committed to supporting access to affordable postsecondary education. This is why the government is also extending the tuition fee freeze at publicly assisted colleges and universities for at least three more years, helping to keep costs down for Ontario students and parents.
Supporting the Financial Sustainability of Ontario’s Postsecondary Sector
Ontario understands the importance of stabilizing the postsecondary education sector to ensure the continued delivery of high-quality educational experiences for students. This is why the government is investing $903 million over three years, starting in 2024–25, to create a Postsecondary Education Sustainability Fund. This investment will include a sector-wide increase to operating grants that will help provide financial stability and predictability for Ontario’s postsecondary institutions, while not raising tuition for Ontario students. This includes $203 million in targeted supports for the financial sustainability of publicly assisted colleges and universities with the greatest financial need.
Through the Postsecondary Education Sustainability Fund, the government will support the continued stability of the postsecondary education system in a responsible way, while building an even stronger foundation for future generations.
Strengthening Accountability and Student Supports
To increase transparency on ancillary fees and other student costs, while also supporting student mental health and keeping campuses safe and inclusive, the government introduced the Strengthening Accountability and Student Supports Act, 2024 on February 26, 2024. If passed, it would authorize the Minister of Colleges and Universities to issue directives requiring colleges and universities to provide information about ancillary fees and other student costs, including for textbooks. This would help students and their families understand the full cost of the courses they are selecting.
If passed, the Strengthening Accountability and Student Supports Act, 2024 would also require colleges and universities to have mental health policies in place that should include clear and transparent information about programs and supports available to students, along with policies to address racism and hate, including but not limited to antisemitism and Islamophobia.
Supporting Small, Northern and Rural Postsecondary Institutions
To ensure that small, Northern and rural colleges and Northern universities can provide students with competitive choices for local postsecondary education, the government is providing an additional $10 million in funding through the Small, Northern and Rural Grant for colleges and the Northern Ontario Grant for universities in 2024–25. The funding is intended to provide targeted support to eligible institutions that are financially vulnerable, while the government works with them on efficiency initiatives.
Reducing Red Tape
Since 2018, Ontario has taken over 500 actions to reduce regulatory burdens — all without compromising health and safety in the population, or the environment.
These changes have helped to open doors to new economic opportunities and reduce unnecessary burdens for individuals and businesses, saving $939 million in gross annual compliance costs that would have otherwise been incurred by businesses, not-for-profit organizations and the broader public sector. Ontario’s Fall 2023 Red Tape Reduction package alone is estimated to save people and businesses over 100,000 hours of time each year.
The government reports on the progress to reduce red tape in the annual Burden Reduction Report. The 2023 Burden Reduction Report: Delivering Better Services and a Stronger Economy highlights how the government is reducing burdens and costs for people and businesses in Ontario, including:
- Creating new ways for individuals to receive medical care in their community;
- Making the online process easier for the application, replacement and renewal of accessible parking permits;
- Upgrading the ServiceOntario appointment booking system to book multiple services in a single appointment or a single appointment for the whole family;
- Streamlining housing development approvals; and
- Helping municipalities better manage restrictions on roads (load periods), including shortening their duration when conditions permit, to support lower costs and better delivery times for the trucking and agri-businesses industry.
These accomplishments are part of Ontario’s efforts to save time and costs for people and businesses.
Strengthening Provincial Agencies
Ontario’s 156 provincial agencies deliver important public services to individuals, families and businesses across Ontario — services such as managing home care, protecting drinking water and Ontario’s food supply, and ensuring the province’s energy infrastructure is reliable and sustainable. Provincial agencies such as Supply Ontario and the Building Ontario Fund are transforming how the government buys goods and services, as well as funds vital infrastructure projects.
This is why the government is strengthening oversight of provincial agencies to ensure that public services are modernized and accountable. The government is introducing new measures and reporting requirements to ensure provincial agencies are efficient, sustainable and accountable while also being nimble to meet the demands of the public they serve. This includes supporting improved service delivery, protecting data and privacy, and aligning agency business strategies with government priorities such as the Community Jobs Initiative announced in the 2022 Budget.
In this way, the government is ensuring the public services that the people of Ontario rely upon are delivered in an effective way for years to come.
Expanding Protected Areas and Provincial Green Spaces
The people of Ontario are passionate about the great outdoors and the natural spaces that communities offer.
Providing More Opportunities to Enjoy Ontario Parks
Ontario is building stronger and healthier communities by expanding recreational opportunities for families to enjoy. This is why the government is actively taking steps to open the first new, all-season, operating provincial park in 40 years. The Bigwind Lake Provincial Park, located near the Town of Bracebridge, will offer facilities and recreational activities including swimming, hiking, cross‐country skiing, and add around 250 new campsites to the Ontario Parks system.
The government is also creating the province’s first urban provincial park in the Township of Uxbridge, which will serve as a year-round day-use provincial park and support the Ontario’s progress on its commitment to provide families with more outdoor recreational opportunities while conserving and protecting areas of natural and scientific interest. A survey was conducted in summer 2023 to seek public input on the programming and activities that could be enjoyed in the proposed park. The government will also explore further opportunities for partnerships for additional urban parks for the people of Ontario.
Improving and Expanding Ontario Parks
Furthermore, the government is enhancing recreational opportunities for the people of Ontario by also implementing a number of other initiatives, including bringing electrical services to over 800 campsites and creating approximately 300 new campsites across several provincial parks.
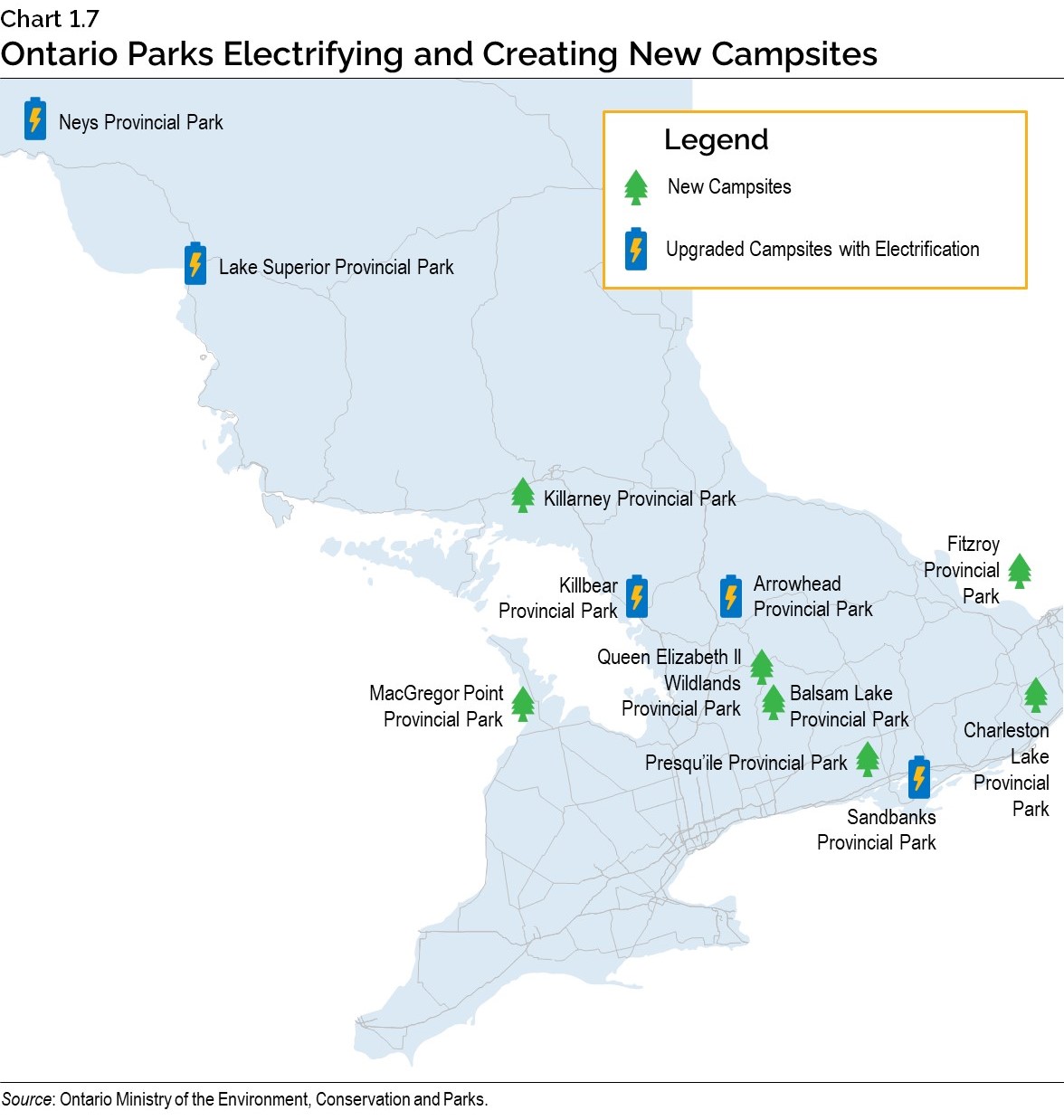
Strengthening Conservation Partnerships
Spending time in nature and green spaces has a positive impact on a person’s health and well-being. The government is committed to continuing to work with partners and conservation leaders to preserve more areas of significant ecological importance, protect natural areas and promote the importance ofhealthy, natural spaces. The government is continuing the Greenlands Conservation Partnership program by investing an additional $20 million over four years. The investment will allow conservation partners to raise matching private‐sector contributions to secure new, privately owned natural areas, such as wetlands, grasslands and forests, as well as ensure they are protected and managed for the future.
Protecting Ontario Lakes
Protecting Ontario’s lakes is a key commitment in the government’s plan to help ensure a safe, healthy and clean environment now and for future generations. The Holland Marsh area produces more carrots, celery, onions, lettuce and greens than any other single region across Canada. The government is supporting farmers to implement technologies and food washing processes that reduce the amount of phosphorus in the water that flows into Lake Simcoe.
The government is continuing to protect and restore the Great Lakes through annual investments of $6.4 million to support innovative projects. These projects are led by community-based organizations, small businesses, municipalities, conservation authorities and Indigenous communities, which focus on protecting and restoring coastal, shoreline and nearshore areas of the Great Lakes and connecting rivers and streams.
Ontario is also investing over $24 million towards the innovative Lake Simcoe Phosphorus Reduction Strategy for a new phosphorus recycling project to help reduce phosphorus discharges from the Holland River into Lake Simcoe.

Protecting You and Your Family
Fighting Criminals With New Air Support
Violent crime within the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) has been increasing in volume, scope and complexity in recent years. To address this challenge, the government is investing $46 million over three years to support patrol and improve response times to major incidents and serious crimes, including the purchase of four helicopters.
These additional resources will help protect communities by:
- Keeping highways and roadways safe from street racing, impaired driving, violent carjacking and automobile theft;
- Locating missing persons, including children, the elderly and vulnerable people;
- Apprehending high-risk suspects, including perpetrators of violent crime; and
- Supporting marine units and enhancing search and rescue capacity.
Public safety is a top priority for this government. This initiative builds on the government’s ongoing commitment to enhance public safety in Ontario by continuing to help ensure that police services have the resources they need to respond to major incidents and urgent situations.
Fighting Auto Theft
Auto theft is a serious and growing problem impacting jurisdictions across Canada, especially Ontario. To combat auto theft, the government is collaborating with municipalities and the federal government, providing funding to police services and raising public awareness of auto theft prevention measures.
The government’s plan includes $49 million over three years to help police put those responsible for auto thefts behind bars. These investments support the Ontario Provincial Police (OPP) Organized Crime Towing and Auto Theft Team, which is working with municipal police services to identify, disrupt and dismantle organized crime networks participating in vehicle theft. In addition, Ontario’s Major Auto Theft Prosecution Response Team provides dedicated support to the OPP to prepare and prosecute complex cases, ensuring that offenders are held accountable.
This funding also continues support for the Greater Toronto Area-Greater Golden Horseshoe Investigative Fund, which was created to help stop the illegal export of stolen vehicles and target violent crime linked to criminal organizations.
Ontario is also continuing prevention and public awareness initiatives to combat auto theft. The Preventing Auto Thefts Grant provides funding to police services for projects that feature new and enhanced crime-fighting measures focused on prevention, detection, analysis and enforcement. In addition, the Financial Services Regulatory Authority of Ontario (FSRA) will be launching an anti-auto-theft campaign that focuses on consumer awareness and auto theft prevention.
The government is combatting auto theft by helping to prevent thefts before they happen, targeting organized crime networks, and ensuring that those responsible are brought to justice to keep people and communities safe.
Protecting the Health and Safety of Firefighters
The government is committed to keeping communities safe and supporting the province’s firefighters. Firefighters are more likely to experience health problems because of exposure to hazardous chemicals. To keep first responders and Ontario’s communities safe, fire departments need resources to ensure they have the right infrastructure and protective equipment.
This is why the government is investing $30 million over the next three years to launch the Fire Protection Grant. This application-based grant will provide municipal fire departments, including in those small and rural communities, with funding for personal protective equipment and specialized decontamination tools to clean and sanitize firefighter gear and mitigate the long-term effects of exposure to chemicals and other fire-related contaminants.
The Fire Protection Grant will support departments by ensuring they have the right infrastructure and protective equipment to respond to local needs and that they may do so safely and more effectively.
Improving Response Times for First Responders
The government will continue working to enable seamless communication between fire and paramedic dispatch systems across the province. This technology will enable municipalities with tiered response agreements to implement simultaneous notification between their fire and paramedic services. This will facilitate faster response times, drive better patient outcomes and enhance Ontario’s public safety response model for the people of this province.
The government is working to ensure that simultaneous notification between fire and paramedic services is operational in the near future in Halton Region, while working on provincial implementation.
Preventing Gender-Based Violence
The government is taking action to help end gender-based violence. Building on existing investments of $1.4 billion over four years, the government is providing an additional $13.5 million over three years to enhance initiatives that support women, children, youth and others who are at increased risk of violence or exploitation — such as Indigenous and racialized communities, and children and youth in the child welfare system. These initiatives include:
- $6 million over three years to support the Children at Risk of Exploitation (CARE) Unit in Kenora District with increased access to trauma-informed specialized supports for children and youth who have been sex trafficked;
- $4.5 million over three years in additional funding for the Victim Quick Response Program+ to increase access to basic necessities for victims of human trafficking and gender-based violence and their families, especially those in Northern, rural and remote communities;
- $2.5 million over three years in additional funding to increase outreach to children and youth with involvement in the child welfare system and link them with resource and educational supports; and
- $0.5 million in 2024–25 to increase training for workers in the child welfare sector to help them respond to human trafficking and identify at-risk children and youth.
This funding will support the government’s commitments under the Anti-Human Trafficking Strategy to protect children and youth, build safer and healthier communities, and support women’s well-being.
Supporting Victims and Survivors of Sexual Assault and Domestic Violence
The government is also investing $27 million over three years to enhance sexual assault and domestic violence services across the province to help victims and survivors receive compassionate and professional support directly within hospital settings.
Ontario is home to a network of 37 Sexual Assault/Domestic Violence Treatment Centres that are dedicated to delivering comprehensive, trauma-informed care and treatment to individuals impacted by sexual and domestic violence. This investment will provide the treatment centres with additional clinical resources and extend the reach of sexual and domestic violence services to hospitals currently not in the network. It will also support the expansion of the Provincial Sexual Assault/Domestic Violence Navigation Line to provide 24/7 care for victims and survivors.
In addition, Ontario is investing $6.4 million over three years to support the Independent Legal Advice for Survivors of Sexual Assault program, and sustain and expand the Child Victim Witness Support Program. These programs provide legal support for survivors of sexual assault and for children who are victims or witnesses of crime. Participation in these programs allows recipients to better understand the criminal court process and make informed decisions about their legal options, including reporting the incident and holding the offenders to account after experiencing sexual assault.
Through these measures, the government is dedicated to building a stronger, more accessible network of support for survivors of sexual and domestic violence across Ontario, ensuring that every individual has access to care and support when they need it.
Combatting the Illegal Cannabis Market
Since the legalization of cannabis in 2018, Ontario has moved forward with rules to keep cannabis out of the hands of children and youth and keep roads safe. The government is committed to combatting the illegal cannabis market to ensure the integrity of the regulated private retail model and address the significant health risks associated with illegal cannabis products that do not meet government safety standards.
This is why the government is investing $31 million over the next three years to support the Provincial Joint Forces Cannabis Enforcement Teams (PJFCET). The PJFCET is an OPP-led centralized enforcement unit that has a proven track record in enforcement operations against illegal cannabis storefronts. This investment would enable the PJFCET to respond to the challenge of illegal online operators and crack down further on the production, sale and distribution of illegal cannabis in the online and offline space.
Modernizing and Enhancing Tobacco Tax Oversight
The 2023 Budget committed to proceed with a review to modernize the Tobacco Tax Act. The government is now proposing changes that would strengthen oversight and reduce burden on registrants. The government remains committed to addressing contraband tobacco and recognizes that it is a persistent challenge in Ontario.
To better address this issue, the government is proposing to strengthen fines in the Tobacco Tax Act to help tackle contraband tobacco while also providing the Ontario Ministry of Finance with the tools to be a modern regulator. Continued support to the OPP Contraband Tobacco Enforcement Team will help disrupt the links between organized crime and contraband tobacco.
Better administration can occur when government uses its resources more effectively. In the case of tobacco, the Ontario Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Health will begin partnering in 2024 on an initiative to cross designate inspectors to seize certain tobacco products in contravention of both the Tobacco Tax Act and the Smoke-Free Ontario Act, 2017. This will allow inspectors to take a coordinated approach, to help address unregulated tobacco while also meeting the requirements under the Smoke-Free Ontario Act, 2017.
The government is committed to making it easier to comply with administrative requirements. For instance, beginning in July 2024, it is proposing to move the monthly filing deadline for tobacco tax registrants from the tenth to the twenty-eighth of each month to allow registrants more time to file and to align with other tax filing deadlines that registrants must also comply with. The Ontario Ministry of Finance is also working towards improving the overall online experience for registrants, making the filing process easier and more efficient.
Moving forward, the review will continue to engage with stakeholders and First Nations partners to identify additional opportunities to modernize the Act, strengthen oversight and align the legislation to the changing tobacco marketplace.
Modernizing Financial Services and Capital Markets to Protect Consumers
Supporting Ontario Credit Unions’ Access to Emergency Lending Assistance
Ontario’s credit unions and caisses populaires play an important role in extending financial services to people and businesses in urban and rural communities across the province. Ontario credit unions manage assets of about $95 billion, employ about 9,000 staff and serve approximately 1.8 million members through almost 550 locations. To support their ability to compete and help ensure broader market stability, it is important to enable direct access to the Bank of Canada’s emergency liquidity facilities for Ontario credit unions. The provincial government is encouraged by the proposal in the federal 2023 Fall Economic Statement to amend the Canadian Payments Act, which would allow eligible provincially regulated credit unions direct access to the Bank of Canada’s Standing Term Liquidity Facility and its Emergency Lending Assistance, and looks forward to ongoing collaboration as changes are being implemented.
Protecting Investors and Enhancing Enforcement in Capital Markets
The government supports the ongoing work of the Ontario Securities Commission (OSC) to modernize the dispute resolution framework available to Ontario investors and remains committed to a modernized capital markets framework that protects investors. This is why the OSC is working to develop rules governing the distribution of disgorged funds to harmed investors. Furthermore, the recently enhanced protections for whistleblowers are intended to encourage individuals to come forward to report misconduct. These measures support enforcement efforts and help increase investor confidence in Ontario’s capital markets.
Footnotes
[1] CMHC Starts and Completions Survey (by intended market, for population centres of over 10,000).
Chart Descriptions
Chart 1.5: Select Measures That Provide Relief to Families and Individuals
The bar chart shows select measures that provide relief for Ontario’s families and individuals in the 2023–24 fiscal year. Government actions would total $8.4 billion for families and individuals in the 2023–24 fiscal year. This includes housing initiatives ($109 million), child care initiatives and child benefits ($583 million), education initiatives ($785 million), transit and transportation initiatives ($1,900 million), energy initiatives ($2,143 million), and initiatives to support vulnerable populations ($2,894 million).
Housing initiatives include the provincial contributions to Ontario's Housing Supply Action Plan. Child care initiatives and child benefits include the Ontario Child Benefit (OCB) indexed to inflation and program growth; Ontario’s contribution to the Canada-wide Early Learning and Child Care Agreement; and the Childcare Access and Relief from Expenses (CARE) Tax Credit. Education initiatives include a 10 per cent tuition fee reduction and subsequent freeze for postsecondary students and its extension. Transit and transportation initiatives include eliminating and refunding fees from licence plate renewal and vehicle validation tags; fee freeze on driver’s licence, tests, and vehicle validation and subsequent annual fee increase cancellation; removing double fares for GO Transit and increasing the PRESTO discount for postsecondary students (Fare and Service Integration); removing tolls on Highways 412 and 418; and cutting gas tax and fuel tax rates. Energy initiatives include cancelling the cap-and-trade carbon tax and also includes ongoing funding for the Ontario Electricity Support Program (OESP). Initiatives to support vulnerable populations include increases to the Ontario Disability Support Program (ODSP) core allowances and Assistance for Children with Severe Disabilities (ACSD); the temporary doubling of the Ontario Guaranteed Annual Income System (GAINS) payments; the Low-income Individuals and Families Tax (LIFT) Credit and its enhancement; the Ontario Seniors Care at Home Tax Credit; OHIP+ and the Ontario Drug Benefit (ODB) Program reform for children and youth without a private plan; expanding the Home and Vehicle Modification Program; expanding the Assistive Devices Program for Continuous Glucose Monitors and Supplies; the Ontario Seniors Dental Care Program; the Ontario Community Support Program; the Shelters and Homelessness Operating Support component of the Toronto new deal; and the Homelessness Prevention Program and Indigenous Supportive Housing Program.
Notes: Numbers may not add due to rounding. Impacts on families and individuals will vary significantly since programs have different eligibility criteria.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Finance.
Chart 1.6: Ontario’s Non-Resident Speculation Tax Timeline
- April 2017: Ontario introduces the Non-Resident Speculation Tax (NRST) in the Greater Golden Horseshoe region at a rate of 15 per cent;
- March 2022: Ontario expands the NRST to apply provincewide, eliminates loopholes and increases the rate to 20 per cent, making it the most comprehensive tax of its kind in Canada;
- October 2022: To further prioritize Ontario families and homebuyers, Ontario increases the NRST rate to 25 per cent; and
- March 2024: Ontario further strengthens the NRST with amendments to support compliance and improve fairness.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Finance.
Chart 1.7: Ontario Parks Electrifying and Creating New Campsites
This map illustrates the locations of the provincial parks where the new campsites will be created, and highlights the following parks:
- Killarney Provincial Park;
- Queen Elizabeth II Wildlands Provincial Park;
- MacGregor Point Provincial Park;
- Balsam Lake Provincial Park;
- Presqu’ile Provincial Park;
- Fitzroy Provincial Park; and
- Charleston Lake Provincial Park.
The map also illustrates the following parks that will be upgraded for campsite electrification:
- Sandbanks Provincial Park;
- Killbear Provincial Park;
- Lake Superior Provincial Park;
- Neys Provincial Park; and
- Arrowhead Provincial Park.
Source: Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Conservation and Parks.