For too long, manufacturing in Ontario was on a path of decline with job losses and low wage growth. Chronic underinvestment in critical infrastructure such as highways resulted in worsening congestion for families and businesses. The government’s plan to build is reversing this course and charting a new way forward. Ontario is attracting record manufacturing investments, and jobs and wages in the province are growing. The government is delivering on the most ambitious capital plan in the province’s history, by investing more than $191 billion over the next decade to build and improve transit, highways, housing-enabling infrastructure, hospitals, schools, long-term care facilities and other critical public infrastructure. However, there is more to be done, and the government must remain bold and ambitious with its plan for building Ontario.
Rebuilding Ontario’s Economy
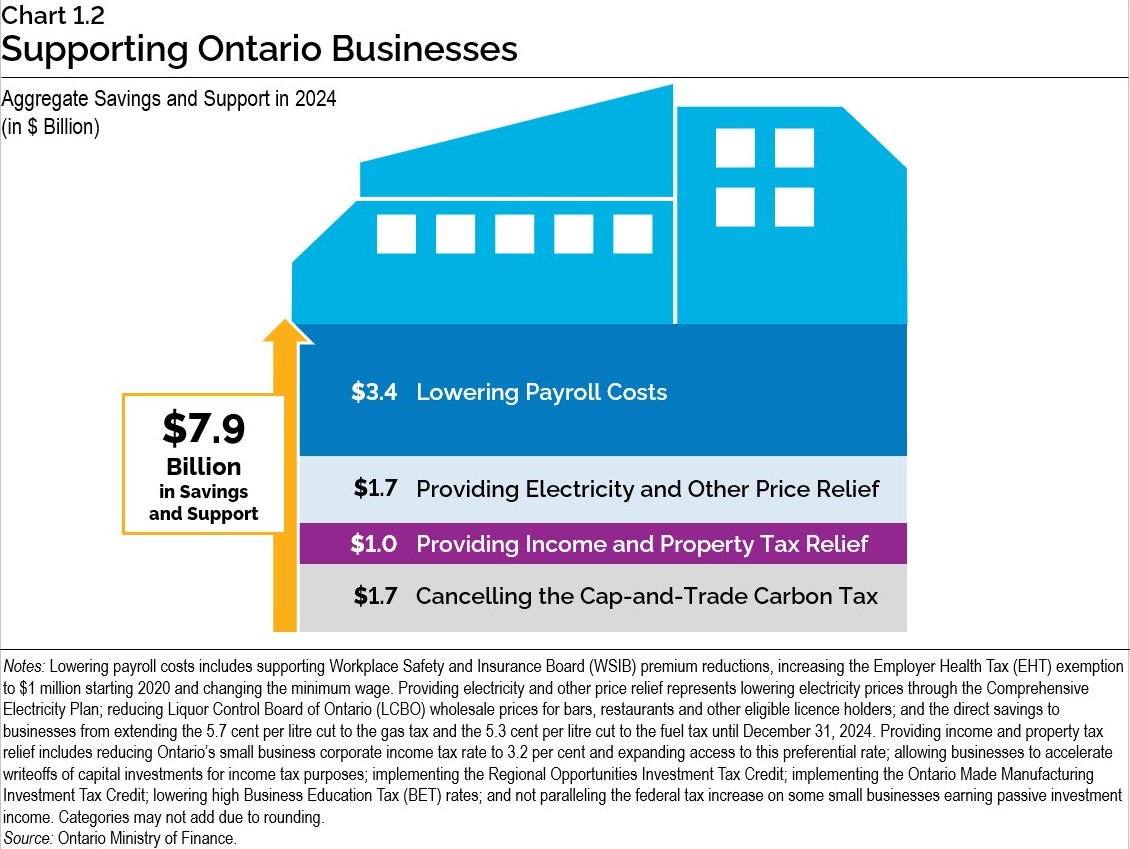
Ontario is working to build a growing and competitive economic environment, despite ongoing challenges including high interest rates and geopolitical uncertainty. Amid these economic challenges, the government is strengthening its economy for the future. The government is helping keep costs down for businesses by enabling nearly $8 billion in cost savings and support in 2024. Ontario is continuing to take a fiscally responsible approach towards attracting investments that build the province’s end-to-end electric vehicle supply chain and to bring manufacturing jobs back to the province. Ontario is also unlocking the critical resources to supply its industries and building the critical infrastructure needed to get them there while supporting a rapidly growing population. To support Ontario’s industries, the government is investing in and securing reliable and affordable energy produced right here in Ontario for decades to come.

Bringing Good Manufacturing Jobs Back to Ontario
For two decades, Ontario’s manufacturing sector experienced a steep decline in employment and output. This was driven by global competitive pressures and the growth of global supply chains, with firms outsourcing their non-core functions abroad. Between the sector’s peak in 2004 and 2018, over 300,000 manufacturing jobs were lost.
Since then, manufacturing in the province has shown progress and Ontario now employs over 800,000 workers in manufacturing. In recent years, employment in the sector has increased significantly, growing by 75,400 between 2020 and 2023. Ontario’s manufacturing sector represented 11.2 per cent of the province’s gross domestic product (GDP) in 2023 and employed 10.2 per cent of Ontario’s total workforce.
The government will continue supporting the progress of rebuilding Ontario’s manufacturing sector and emerging growth industries such as technology and life sciences, by pursuing more investments and enhancing the province’s strong business climate. This work is even more important given the uncertainty in international trade and the need to secure Ontario’s supply chains.
Creating the Conditions to Grow the Manufacturing Sector
In April 2023, the government established an Advanced Manufacturing Council to inform a strategy that would help boost the long‐term competitiveness and resilience of the manufacturing sector. The council was instrumental in the development of an Ontario made manufacturing plan.
The Advancing Ontario Made Manufacturing Plan is a 10-year roadmap for growing the sector’s workforce and production capacity, by securing next-generation production facilities, strengthening and securing domestic supply chains, leveraging growth-driving technology and building a workforce for the future. The objectives of the plan are to help grow the sector’s output to over $120 billion and expand Ontario’s manufacturing workforce to one million people by 2035.
The plan includes new investments to extend the Advanced Manufacturing and Innovation Competitiveness (AMIC) Stream of the Regional Development Program, and funding to expand the Ontario Made program. It will also leverage key existing initiatives to attract manufacturing investments such as the Ontario Made Manufacturing Investment Tax Credit and programs to unlock new opportunities for the sector, including the Ontario Centre of Innovation’s (OCI) Critical Industrial Technologies Initiative. Moving forward, the government will continue to find ways to support the economy and grow manufacturing by attracting investments and increasing the sector’s competitiveness and resilience.
Lowering Taxes to Help Local Manufacturers Invest More
As part of the Advancing Ontario Made Manufacturing Plan, the province continues to offer the Ontario Made Manufacturing Investment Tax Credit to help lower costs for manufacturers. Introduced in the 2023 Budget, this tax incentive is a 10 per cent refundable corporate income tax credit that is available for eligible investments in buildings, machinery and equipment for use in manufacturing or processing in the province. An eligible Canadian-controlled private corporation could receive Ontario income tax support of up to $2 million a year.
From 2023–24 to 2026–27, estimated support of $1.1 billion will be provided to eligible Ontario manufacturers, helping to lower their costs, encourage innovation and enhance competitiveness.
The government continues to review the support provided by the Ontario Made Manufacturing Tax Credit to ensure its accessibility and effectiveness.
Investing in Competitive and Innovative Companies
In 2022, the government launched the Advanced Manufacturing and Innovation Competitiveness (AMIC) Stream under the Regional Development Program to build on the province’s competitive advantages in the manufacturing sector. As part of the Advancing Ontario Made Manufacturing Plan, the government is providing an additional $40 million to extend the AMIC Stream starting in 2025–26.
The AMIC Stream provides funding of up to 15 per cent of eligible project costs, as well as complementary services and supports in the advanced manufacturing sectors, including automotive, aerospace, chemical, information and communications technology (ICT), life sciences and steel. The continuation of the AMIC Stream focuses on fostering growth in small and medium-sized enterprises and reinforcing supply chains across Ontario by supporting investments in capital equipment, promoting technology adoption and fostering skills development.
Expanding the Ontario Made Program

In July 2020, Canadian Manufacturers & Exporters (CME), with support from the government of Ontario, launched the Ontario Made program to help make it easier for consumers and supply chain partners to identify and purchase products made in Ontario. Since then, CME has registered over 17,000 products on their online database, sourced from over 4,400 Ontario manufacturers across the province.
The government is investing $500,000 to expand the Ontario Made program starting in 2025–26, to provide young people with increased exposure to career opportunities in the manufacturing sector through activities such as open doors events at manufacturing facilities.
Helping Companies Adopt New Critical Technologies
The application of technologies such as 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, robotics, cybersecurity and quantum help increase productivity and drive growth. These technologies are critical to the success of Ontario industries as global competition intensifies among businesses that are leveraging these innovations.
In March 2024, the Ontario Centre of Innovation launched the Critical Industrial Technologies (CIT) Initiative, leveraging an investment of $50 million by the government of Ontario. This initiative aims to support the integration of critical technologies into key sectors of the economy. Examples of critical technologies may include the use of robotics to optimize manufacturing production processes, as well as cybersecurity in agri-food facilities to protect against disruptions in food production and processing. The investment will help equip Ontario businesses, including sectors such as advanced manufacturing, construction, mining and agri-food, with technologies to boost competitiveness.
Securing New Investments Through Invest Ontario
Since its inception in 2020, Invest Ontario has served as a one-stop shop to investors for business information and tailored investment solutions, including talent support, advisory assistance and concierge services. The investment attraction agency provides facilitated access to all levels of government and local service providers, as well as financial assistance through the Invest Ontario Fund to support investments in key industries such as advanced manufacturing, life sciences and technology. To date, Invest Ontario has helped attract $4.1 billion in investments, which are expected to create 4,012 jobs.
To continue attracting major investments to the province, the government is allocating an additional $100 million to the Invest Ontario Fund. This builds on the $100 million announced in the 2024 Budget and brings the fund total to $700 million. The additional funding will further support Invest Ontario in securing strategic investments that create jobs and drive Ontario’s long-term economic growth and global competitiveness.
As part of its investment attraction efforts, Invest Ontario also unveiled its new Partner Portal in August 2024. The portal supports investors as they consider starting or expanding a business in Ontario by providing a one-stop online resource that centralizes information on industrial sites, demographic data, and provincial resources.
Making Ontario a Global Leader of Electric Vehicle Manufacturing
Ontario’s auto sector is a significant part of the provincial economy, employing nearly 100,0001 workers in 2023 and supporting thousands more jobs throughout the supply chain, which includes over 700 parts firms; over 500 tool, die and mould makers; and over 400 companies focused on connected and autonomous vehicles.
As Ontario’s auto sector transforms as part of the transition to electric vehicle (EV) production, it has attracted more than $44 billion in investments over the past four years from global automakers, parts suppliers, and manufacturers of EV batteries and battery materials. These investments are helping to create over 14,000 new jobs in communities across the province, plus thousands more across the supply chain. With the investments Ontario has attracted across the EV assembly, battery cell and the battery component supply chain, the province ranks second only to Michigan in North America in terms of EV-related investment attraction. Ontario has recently supported the following investments to continue to build the province’s end-to-end EV supply chain:
- In April 2024, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., along with joint venture partners, announced an investment of approximately $15 billion to build four new manufacturing plants in the province, including:
- An innovative and world-class electric vehicle assembly plant, the first of its kind for Honda;
- A new stand-alone electric vehicle battery manufacturing plant at Honda’s facilities in Alliston;
- A processing plant for cathode active materials (CAM) and a precursor to CAM (pCAM) through a joint venture partnership with POSCO Future M Co., Ltd. These materials are the main components of cells for lithium-ion batteries; and
- A separator plant through a joint venture partnership with Asahi Kasei Corp., as mentioned below.
- In August 2024, Goodyear Canada Inc. announced a $575 million investment to modernize and expand its tire manufacturing plant in Napanee, which is expected to create 200 new, highly skilled manufacturing jobs by 2027 and secure more than 1,000 jobs. This investment will help Goodyear create an energy-efficient, end-to-end manufacturing process and increase its production capacity, including EV and all-terrain tires.
- In May 2024, Asahi Kasei Corp. announced it would invest approximately $1.6 billion to build its separator plant in Port Colborne, which is expected to become commercially operational in 2027. Separators are an essential component of an EV battery.
In addition, Volkswagen is investing $7 billion to establish its first overseas EV battery cell manufacturing plant in St. Thomas and will create 3,000 jobs. The plant is expected to be completed in 2027 and will produce battery cells for up to one million EVs per year.
Stellantis N.V. and LG Energy Solution are also partnering to invest more than $5 billion towards the NextStar Energy EV battery cell manufacturing plant in Windsor, helping to support an estimated 2,500 jobs. The plant is expected to be fully operational in 2025 and be the first large‐scale, domestic, EV battery cell manufacturing facility in Canada.

Encouraging the Adoption of Electric Vehicles
Expanding the electric vehicle charging network and reducing costs for charging infrastructure are critical to making charging more affordable and accessible for families across the province, including rural Ontario. Ontario is taking steps to help encourage EV adoption in the province and support the province’s electric vehicle manufacturing industry.
Through the EV ChargeON program, the government is investing $91 million to make it easier to access EV chargers. This includes installing EV charging stations in small and medium-sized communities across the province. In June 2024, the government issued a Request for Bids to build and operate EV charging stations on provincial lands in underserved and remote communities, including highway rest areas, carpool parking lots and provincial parks. The Request for Bids period closed on September 26, 2024, and bids are currently being evaluated. In addition, more than 80 level 3 fast chargers are being installed across all 23 ONroute locations as part of the Ivy Charging Network. Each location will have between two and four chargers to service electric vehicle drivers. Expanding the charging network will address range anxiety and make it more convenient for drivers to access EV chargers outside of large urban centres.
In May 2024, Ontario announced it is also exploring options to reduce electricity rates for public EV charging providers in areas where demand is beginning to emerge. The new Electric Vehicle Charger Discount Electricity Rate will be available for public EV charging providers on January 1, 2026.
Driving Growth in the Life Sciences Sector
With Ontario being home to the largest life sciences sector in Canada, there is a significant opportunity for the province to capitalize on this large and growing sector. The government is planning to help grow the sector by harnessing the province’s strengths in manufacturing, such as the production of medical isotopes; research and development; science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) talent, as well as Ontario’s robust network of innovative startup companies to optimize life sciences innovation and benefit Ontario’s health care system.
Ontario is delivering on this plan through its Life Sciences Strategy, Taking Life Sciences to the Next Level, to help secure the province as a global biomanufacturing and life sciences hub. The Life Sciences Strategy will position the province for greater innovation and biomanufacturing capacity while aiming to increase employment to 85,000 high-value jobs in the sector by 2030, from over 72,000 workers in 2022.
As part of Phase 1 of the Life Sciences Strategy, the government focused on addressing immediate sector challenges, including growing manufacturing, boosting commercialization capacity and increasing the adoption of innovations for health care. The province has made progress by attracting over $5 billion in investments and creating 5,000 jobs in the life sciences sector since 2018.
To support the development of Phase 2 of the Life Sciences Strategy, Ontario convened an industry-led Life Sciences Council in 2023 to inform an all-of-government approach focused on long‑term growth and emerging areas of opportunity for the sector. In October 2024, the government announced its investment of $146 million to launch Phase 2 of the Life Sciences Strategy to help fuel sector’s growth. This includes the investment of $94 million over eight years starting in 2024–25 to implement six initiatives:
- Up to $46 million to strengthen Ontario’s research, innovation and biomanufacturing capacity by launching a new program under the Ontario Research Fund to provide co-funding for projects approved under the federal Biosciences Research Infrastructure Fund Stage 2. This will support advances in next-generation vaccines, therapeutics and diagnostics;
- $15 million to launch a wet labs initiative, which will create a new multi-tenant wet lab space to address the critical shortage for early-stage and pre-commercial companies. In a wet lab, testing and analyses are performed using physical samples, chemicals and liquids;
- $5 million to partner with Clinical Trials Ontario to support the QuickSTART initiative, which will identify and implement ways to reduce the time to get new clinical trials started;
- $24 million to introduce the Life Sciences Scale-Up Fund (LSSUF), aligned with the new Health Innovation Pathway, to enhance domestic manufacturing capacity by providing financial support to help small and medium-sized enterprises scale up and be ready to access procurement opportunities. The LSSUF will also act in tandem with the $12 million Health Technology Accelerator Fund (HTAF), announced in the 2024 Budget, to provide opportunities for innovators, including Ontario companies, to partner with local health care service providers;
- $3 million to launch a Life Sciences Marketing Plan in partnership with Invest Ontario to promote Ontario as a key destination for life sciences investments; and
- $1 million to develop a Life Sciences Ecosystem Asset Map to provide insight into the sector’s strengths and advance the formation of emerging technology domain hubs.
Under Phase 2, these initiatives will build on the government’s commitment of $40 million from the Venture Ontario Fund and the $12 million from the Health Technology Accelerator Fund to help solidify the province as an emerging hub and leader for biomanufacturing and life sciences.

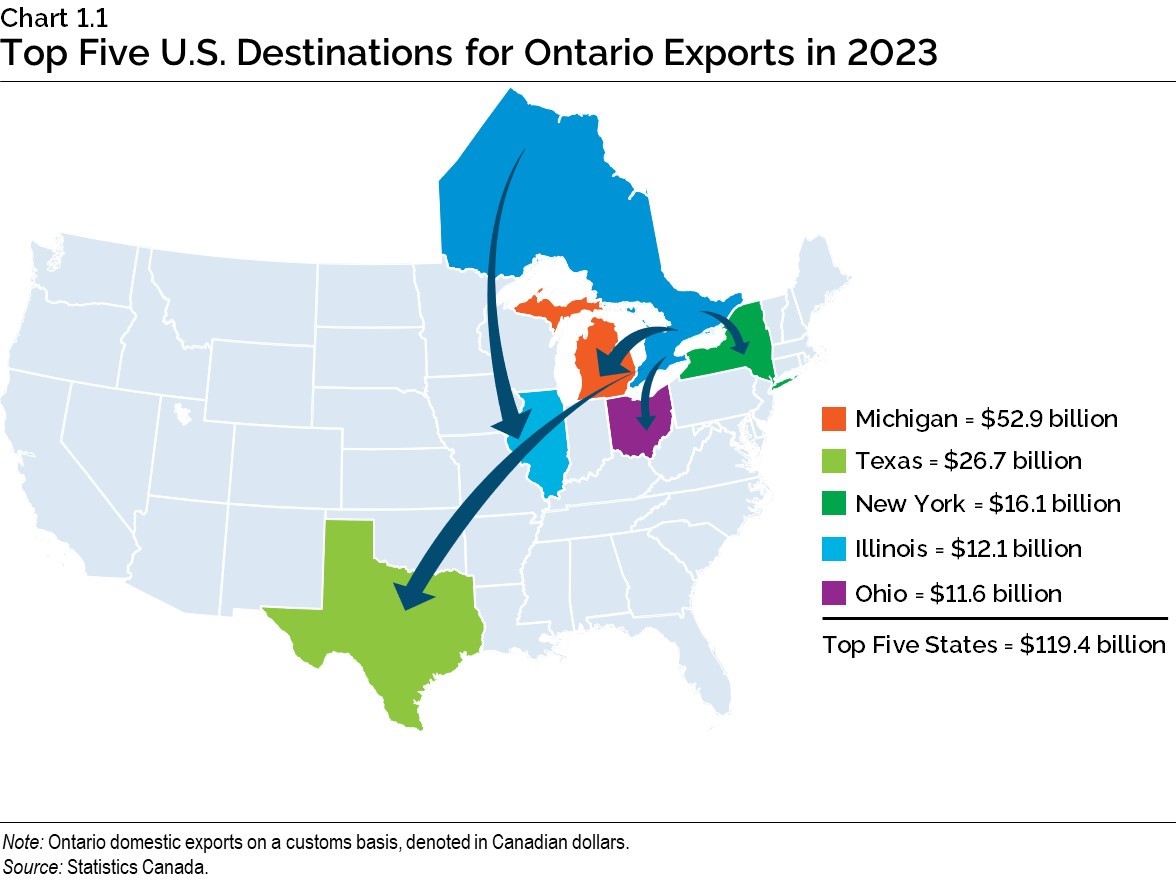
Prioritizing Ontario’s Trade Relations with the United States
In 2023, Ontario’s total trade with the United States was valued at around C$500 billion and the province was the top export destination for 17 states across the United States, while ranking second for 11 others. Ontario is working to enhance trade with its top trading partner to create more business opportunities and jobs on both sides of the border.
Powering Ontario’s Economy
To support the creation of more jobs and the continued growth of the economy, the province’s electricity demand is forecasted to increase at least 75 per cent by 2050. Ontario’s affordable and diverse electricity supply mix gives it an edge in drawing in investments and creating jobs. That is why the government is increasing investments in a future powered by reliable, affordable and clean energy across the province. This investment is crucial for staying competitive and helping Ontario shift towards a clean economy, especially as it attracts investments in areas like manufacturing, mining, electric vehicles, battery production and advanced technologies like artificial intelligence data centres. But those advantages will erode quickly if the government and infrastructure cannot keep up.
Building on Ontario’s Nuclear Advantage
As a world leader with experience and expertise in nuclear energy, Ontario is leveraging its position to develop the next generation of nuclear power. To meet growing electricity demand, and as the government rebuilds Ontario’s economy, Ontario is building on its nuclear advantage, which already provides more than 50 per cent of the province’s power.
The government has also introduced the Ontario Sustainable Bond Framework, enabling Green Bonds to fund environmentally beneficial projects, including emissions-free nuclear energy.
Planning and Building the Future of New Nuclear
The government is working with Ontario Power Generation (OPG) to commence planning and licensing for three additional small modular reactors (SMRs), in addition to an already planned SMR, which has completed the first phase of site preparation at the Darlington Nuclear Generating Station, the first in the G7. Once deployed, these four units would produce enough clean electricity to power 1.2 million homes. The government is also working with Bruce Power on pre‐development work for the first large‐scale nuclear generation build in over three decades in Canada.
Refurbishment of Existing Nuclear Facilities
Pickering Refurbishment
The Ontario government is supporting OPG’s plan to proceed with the next steps towards refurbishing the Pickering Nuclear Generating Station B Units.
Once refurbished, the Pickering Nuclear Generating Station would produce a total of more than 2,000 megawatts (MW) of emissions-free electricity, equivalent to powering two million homes. The Conference Board of Canada’s preliminary analysis estimates this refurbishment would increase Ontario’s GDP by $19.4 billion and create about 11,000 jobs over the 11‐year project period. Post‐refurbishment operation of the facility would also create and sustain about 6,410 Ontario jobs per year for decades to come.
Darlington and Bruce Refurbishments
Ontario continues to support the refurbishments at the Darlington and Bruce Nuclear Generating Stations. With refurbished units, the generating capacity of the stations will provide approximately 3,500 MW and 6,550 MW, respectively, enough to serve about 1.7 million residential customers and 188,000 commercial, industrial and other customers, equivalent to about 36 per cent of the province’s electricity customers.
OPG has already completed refurbishment of two of the four Darlington units and is on track to complete the third unit on time and on budget. The government and OPG have already achieved major milestones on this project by successfully reconnecting Darlington Nuclear Generating Station’s Unit 3 to Ontario’s electricity grid, 169 days ahead of schedule.

Growing Ontario’s Nuclear Supply Chain and Expertise
Ontario’s expansion of nuclear energy is cementing the province’s position as a global leader in new nuclear technologies, creating new export opportunities that will drive economic growth.
- In June 2024, Ontario announced the successful completion of trade missions to Romania and France, securing significant deals totalling $360 million that will leverage the province’s nuclear expertise to create jobs for Ontario workers and grow its nuclear supply chain.
- Ontario is leveraging the expertise of OPG and its subsidiary Laurentis Energy Partners to support a new collaboration agreement with SaskPower in the deployment of a small modular reactor in Saskatchewan that would also create more jobs for the Ontario economy.
- OPG and other Ontario nuclear supply chain providers had previously signed major agreements valued at approximately $1 billion to export nuclear products and services to other countries, including Poland, Estonia and the Czech Republic, while also generating more good-paying jobs at home that support Ontario workers and families.
Investing in Hydroelectric Energy
The Ontario government is expanding and refurbishing clean electricity generation by announcing more than $2.6 billion to refurbish 12 stations across the province, including the Sir Adam Beck Complex at Niagara Falls and the R.H. Saunders Generating Station in Cornwall, the two largest in the province. These investments will secure 4,362 MW of clean electricity generation. Combined, these investments will power 4.3 million homes, helping to meet increasing demand from electrification and fueling the province’s growth.
Supporting Clean Energy Storage Projects
New energy storage projects will support the operation of Ontario’s clean electricity grid by drawing and storing electricity off‐peak when power demand is low, and returning the power to the system during times of higher electricity demand.
In May, Ontario completed the largest battery storage procurement in Canada’s history, securing nearly 2,700 MW, exceeding the government’s initial target of 2,500 MW. When combined with the Oneida Energy Storage Project, Ontario’s entire storage fleet will be comprised of 26 facilities with a total capacity of nearly 3,000 MW.
Launching the Largest Competitive Energy Procurement in Ontario’s History
The Ontario government is launching the largest competitive energy procurement in the province’s history, which will provide affordable electricity for families and businesses. This initiative will secure at least 5,000 MW of electricity resources to meet growing demand for clean and reliable power, as part of a diverse supply mix of nuclear, hydroelectric, renewables, natural gas, and biomass energy sources. The government is exploring options to expand and accelerate this procurement to meet growing energy needs.
The government is committed to make the procurement process transparent, competitive and cost-effective, with a focus on protecting prime agricultural areas and in municipalities that provide consent.
Supporting the Largest Indigenous-Led Energy Project in the Province’s History
The Ontario government and Wataynikaneyap (Watay) Power, a First Nations-led company made up of 24 Indigenous communities, have participated in the largest Indigenous-led and lengthiest grid connection project in Ontario’s history.
Approximately 1,800 kilometres of transmission line have been built by the Watay Power Transmission Project through a government loan of up to $1.34 billion for the project’s construction costs. This will contribute to Ontario’s GDP by connecting communities to affordable electricity and well-paying local jobs. As well, since the project’s conception, nearly 1,000 First Nation members worked on the construction of the line. Ontario is also supporting the First Nations’ equity investment in the project by providing a loan guarantee under the Aboriginal Loan Guarantee Program.
The government is fostering partnerships with Indigenous and First Nation communities to not only support economic growth in the region, but also enhance environmental and health benefits for these communities through emission reductions, enhanced electricity reliability, and the elimination of diesel. The Watay line has been estimated to avoid 6.6 million tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions per year, equivalent to taking almost 35,000 cars off the road.
As of September 2024, 12 remote First Nation communities have been connected to Ontario’s clean energy grid through the project. The project will ultimately connect 18,000 people in 16 remote Indigenous communities to affordable energy.
Extending and Enhancing the Time-Limited Tax Relief for the Electricity Distribution Sector
Electricity distribution companies face challenges to upgrade aging infrastructure, meet Ontario’s evolving electrification and cybersecurity needs, and improve services for customers. The government supports voluntary electricity distribution sector consolidation in an effort to improve efficiency, accelerate the adoption of new technologies, and increase capacity to support Ontario’s growing electricity needs.
In the 2024 Budget, Ontario committed to review existing supports for consolidation of interested municipal electricity utilities (MEUs), and to provide a status update as part of the 2024 Ontario Economic Outlook and Fiscal Review. As a result of this review, Ontario will:
- Extend the existing time-limited tax relief measures for a further four years. This would allow the incentives to continue uninterrupted until December 31, 2028.
- Enhance the Transfer Tax rate relief by setting it to zero per cent for all MEUs for transactions occurring from January 1, 2025, to December 31, 2028. This enhancement to the existing relief is intended to provide a stronger incentive for consolidation activity in the Ontario electricity distribution sector.
Moving forward, Ontario is committed to working with all levels of government to provide support to MEUs to encourage voluntary consolidations, incentivize greater capital investment in infrastructure and ensure better service to customers.
See the Annex: Details of Tax Measures and Other Legislative Initiatives for more information.
Unlocking Ontario’s Resources Sustainably
The government continues to promote growth in the province’s primary sectors, which have vast untapped potential. Ontario is home to enormous mineral wealth, its Crown forests cover almost two-thirds of the province, and it has the largest, most diverse agri-food sector in Canada. These resources feed industries and supply chains across Ontario, including EV batteries, electronics, energy, health and life sciences, construction and agri-businesses. The government is encouraging economic growth partnerships for Indigenous, Northern and rural communities, while ensuring primary resources are managed sustainably.
Strengthening the Critical Minerals Supply Chain
The mining sector is a key contributor to the Ontario economy, as well as an engine for regional economic development. In 2023, Ontario’s mining and extraction sector contributed $6.9 billion to the province’s real GDP and employed 35,400 people, adding 8,600 jobs since 2018. Critical minerals mined in Ontario are used in many high-growth sectors and their supply chains, including electric vehicles, clean energy and information communications technology.
In March 2022, the government released its first-ever Critical Minerals Strategy, which focuses on supporting better supply chain connections between industries, resources and workers in Northern Ontario and manufacturing in the South. As part of this strategy, Ontario launched the $5 million Critical Minerals Innovation Fund (CMIF) in November 2022 to enhance research and development of new technologies. As part of the 2024 Budget, the government announced an additional $15 million over three years to expand the CMIF. To date, the CMIF has invested in 12 industry-led critical minerals innovation projects.
To further support the mining sector and critical mineral exploration, the government announced an additional $6 million over two years for the Ontario Junior Exploration Program (OJEP) in April 2023, bringing the total investment in OJEP to $35 million. This investment included a critical minerals stream, which provides support for companies searching for critical minerals. As of April 2024, Ontario has provided $19.4 million in funding to 133 projects through OJEP.
Ontario is also working to deepen its strategic partnerships with the United States to expand cross-border trade and strengthen a resilient critical minerals supply chain to enhance shared economic security, support the transition to cleaner technologies, and reinforce Ontario’s leadership in the global market for critical minerals.
Making Progress on the Road to the Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire region is a future source of key critical minerals, including chromite, cobalt, nickel, copper and platinum. These minerals play a significant role in supporting innovative technologies, including electronics, electric vehicles and cleantech.
Building the necessary infrastructure in and around the region is a prerequisite to unlocking the potential and lowering the cost of developing future mining projects in the Ring of Fire. Ontario has dedicated $1 billion to support critical infrastructure projects, such as all‐season roads, broadband connectivity and community supports for the Ring of Fire region.
Investment in these roads would also help improve First Nations’ community access to goods and services, including education, health care and housing by connecting them to the Ontario highway network for the first time. The government will continue to support the Environmental Assessments (EAs) for the Marten Falls Community Access Road Project, the Webequie Supply Road Project and the Northern Road Link Project, led by Marten Falls First Nation and Webequie First Nation.
In March 2024, Marten Falls First Nation and Webequie First Nation signed an agreement with Ontario to develop community infrastructure projects that could support future economic development opportunities in the Ring of Fire area. These infrastructure projects will help improve the livelihood and well-being of the First Nation communities in the area, while marking an important step towards realizing the economic potential of the Ring of Fire.
Ontario also signed Letters of Confirmation in June 2024 to support renewed partnerships with Animbiigoo Zaagi’igan Anishinaabek, Aroland First Nation, Ginoogaming First Nation and Long Lake #58 First Nation. Commitments outlined in the Letters of Confirmation include an agreement to upgrade roads that connect First Nation communities to the provincial highway network and contain funding for other community infrastructure and skills training programs for First Nations people.
As Ontario invests in and makes progress on developing critical infrastructure in the Ring of Fire region, the provincial government continues to call on the Government of Canada to match Ontario’s funding commitments and expedite approval processes for all infrastructure that would enable the development of the Ring of Fire and generate considerable economic benefit to Indigenous and Northern communities.
Boosting Economic Development in Northern Ontario
The government continues to support projects in Northern communities through the Northern Ontario Heritage Fund Corporation (NOHFC). The NOHFC fosters economic growth by providing financial assistance to projects that help stimulate job creation and workforce development in the North. Since June 2018, the NOHFC has invested more than $841 million in 6,894 projects in Northern Ontario, leveraging more than $2.5 billion in investment and creating or sustaining over 10,560 jobs.
Supporting Ontario’s Forest Sector and Forest Product Manufacturing
The forestry sector is a significant part of the economy in Northern Ontario and represents a critical source of employment for communities in the region. Ontario’s forest sector produces wood for building homes, furniture, making paper and packaging, and as an energy source. Using mass timber and wood construction for modular and prefabricated buildings will be essential to achieving the government’s goal of building 1.5 million new homes by 2031.
In July 2024, the Ontario government released a proposed action plan designed to expand wood construction in the province. The Advanced Wood Construction Action Plan will help create opportunities in the forest sector by diversifying and growing demand for sustainably harvested wood in Ontario. Advanced wood construction (AWC) uses wood-based prefabricated and modular components that can be assembled off-site and delivered for installation. This can help save time and reduce waste, allowing projects to be completed up to 50 per cent faster and reducing costs by up to 20 per cent. Innovative building materials add value to Ontario’s forest resources, bolstering the economy and creating jobs across the provincial supply chain.
Growing the Agri-Food Sector
Ontario has a rich and diverse agri-food sector that produces over 200 agricultural commodities. With 60 per cent of the food produced in Ontario being consumed right in the province, the agri food industry is an important source of jobs and economic growth. Since 2018, Ontario’s agri-food sector employment has increased by over 27,000, supporting over 871,000 jobs in 2023, representing roughly one in nine jobs in Ontario. As Ontario’s population expands, the demand for agri-food products is expected to grow, creating opportunities to increase local food production to meet this demand. That is why earlier this year, the Ontario government created a dedicated ministry: the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Agribusiness, with a refocus on growing the agri-food sector and helping to create a stronger economy for the province.
In November 2022, the government released Grow Ontario: a provincial agri-food strategy to strengthen the agri-food sector, fuel economic growth through innovations and ensure an efficient and reliable food supply while addressing ongoing vulnerabilities such as changing market conditions or climate-related risks.
Ontario’s Risk Management Program helps to ensure Ontario farmers have long-term confidence so they can compete globally. This $150 million program supports farmers with unforeseen challenges such as fluctuating market prices, extreme weather events like flooding or drought, and disease. The critical supports provided through the program help secure jobs and activity across Ontario’s food supply chain. Ontario will continue to work with the sector to manage the risks that it faces and to help grow the industry. In January 2024, the government announced consultations to help inform the development of a new strategy.
In July 2024, Ontario announced an investment of $7.2 million in 44 Ontario-led research and innovation projects through the Ontario Agri-Food Innovation Alliance, a collaboration between the government, the University of Guelph, and Agricultural Research and Innovation Ontario (ARIO). These projects focus on protecting animal and plant health, strengthening production systems, increasing environmental sustainability, and bolstering productivity and growth.
In September 2024, the government announced an investment of nearly $1.3 million in seven research projects through the Agricultural Research and Innovation Ontario (ARIO) Innovative Breeding Research Program (IBRP). These research projects will help farmers increase their long-term productivity and competitiveness by creating new tailored plant varieties and livestock for the province’s domestic food supply and export markets.
In addition, the government continues to support the Grow Ontario strategy with investments through the Sustainable Canadian Agricultural Partnership (Sustainable CAP). The partnership is a $3.5 billion, 5-year agreement between the federal, provincial and territorial governments that started in April 2023.
Strengthening Shortline Rail Systems in Ontario
Supply chain infrastructure is a critical enabler of economic activity in the province. Ontario has an extensive network of railways that consists of larger national railways as well as shortline railways, many of which are integral to accessing resources and raw materials.
As announced in the 2024 Budget, Ontario is committed to exploring ways to support shortline rail, which plays an important role in the safe and efficient transport of goods and people throughout the province. This will include engaging the federal government on the potential development of a tax credit and exploring tax credit transferability, or alternatively, considering another form of support.
Advancing Home-Grown Research and Innovation
Advancing home-grown research and innovation in Ontario is essential to keep ideas, expertise and intellectual property in the province and support long-term economic growth. In May 2024, the Ontario government announced an investment of nearly $200 million over three years at six leading research institutions in the province to fund cutting-edge discoveries, promote new business opportunities and help foster a highly skilled labour force. This investment includes:
- $144 million over two years for the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research to help research and deliver real-world solutions that find cancer earlier and treat it more effectively;
- $36 million over three years for the Perimeter Institute for research, training and educational outreach in theoretical physics;
- $5 million over two years for Ontario Genomics to lead the application of genomics-based solutions;
- $4 million over two years for Clinical Trials Ontario to strengthen, promote and capitalize on Ontario’s competitive advantage of conducting high-quality clinical trials;
- $4 million over two years for the Fields Institute for research in mathematical sciences; and
- $3 million over two years for Compute Ontario to help realize the potential of digital research infrastructure.
These six research institutes have strong, proven records in fostering research and innovation in a range of critical sectors that are significantly improving the lives of the people of Ontario, including in the life sciences, finance, agriculture, quantum computing and information technology. This funding will help ensure the research sector continues to be a leading contributor of innovation and commercialization in the province, while enhancing Ontario’s productivity and global competitiveness.
Making Ontario Open for Business
For too long, Ontario businesses and entrepreneurs faced unnecessary red tape and a prohibitively high cost of doing business, as key inputs like electricity had significant price increases that stifled growth.
Keeping Costs Down for Ontario Businesses
Since 2018, the government has taken significant actions to lower costs for businesses and help them compete, grow and create good-paying jobs. Through these actions, the government is enabling nearly $8 billion in estimated cost savings and support in 2024 for Ontario businesses, of which $3.7 billion would go to small businesses. Some of the actions taken include:
- Implementing the Ontario Made Manufacturing Investment Tax Credit to help local manufacturers invest and expand, by lowering costs for eligible investments in buildings, machinery or equipment used in manufacturing or processing in the province;
- Temporarily cutting the gas tax by 5.7 cents per litre and the fuel tax by 5.3 cents per litre beginning July 1, 2022, and proposing, for the fourth time, to extend these rate cuts to June 30, 2025, to help reduce the cost of gas and fuel for Ontario businesses;
- Supporting cuts to Workplace Safety and Insurance Board (WSIB) premium rates without reducing benefits, leading to a reduction in payroll costs for businesses;
- Increasing the Employer Health Tax (EHT) exemption from $490,000 to $1 million. The EHT exemption increase helps businesses by reducing the tax for eligible private-sector employers on their total Ontario payroll;
- Cancelling the cap‐and‐trade carbon tax to remove its cost impact from items such as gasoline, diesel fuel and natural gas;
- Lowering high Business Education Tax (BET) rates, providing $450 million in annual savings for over 200,000 employers, or 95 per cent of all business properties in Ontario;
- Reducing the small business corporate income tax rate to 3.2 per cent and expanding access to this preferential rate, helping small businesses compete and thrive by lowering their costs;
- Implementing the Regional Opportunities Investment Tax Credit to support businesses that make investments and expand in regions of Ontario that have lagged in employment growth;
- Allowing businesses to accelerate writeoffs of capital investments for income tax purposes, to support businesses that make eligible investments across Ontario; and
- Implementing the Comprehensive Electricity Plan in January 2021, which is lowering electricity costs by an estimated average of 13 to 16 per cent in 2024 for medium‐sized and larger industrial and commercial customers, respectively.
Cutting Red Tape
Since 2018, Ontario has taken over 500 actions to save time and money for people, businesses, not‑for-profit organizations, municipalities, universities and colleges, school boards and hospitals. Through these actions, the government has eliminated over $1 billion in annualized compliance costs for businesses, not-for-profit organizations, and the broader public sector since 2018.
In spring 2024, the government passed a new Red Tape Reduction Package, including the 12th red tape reduction bill introduced by Ontario since 2018. The Cutting Red Tape to Build More Homes Act, 2024 eliminates red tape and helps to speed up government processes in support of the government’s commitment to build at least 1.5 million homes by 2031. The legislation and targeted housing measures would help municipalities, industry and people in Ontario to:
- Build homes faster at a lower cost, including by letting homebuyers and homebuilders decide on the number of parking spaces in a new residential development near transit based on market needs, and by making it easier to build more garden, laneway and basement suites;
- Prioritize ready-to-go housing projects with a new “use it or lose it” process to address stalled development; and
- Build more types of homes for more people by streamlining approvals for student housing, supporting standardized designs to reduce delays and costs, including for factory-built housing, and supporting innovative construction methods, such as mass timber.
Helping Entrepreneurs Start and Grow their Business
Through Ontario’s network of 54 Small Business Enterprise Centres, the Starter Company Plus program provides training, mentoring and business advice alongside a grant to help ensure entrepreneurs have the support they need to grow their business.
In May 2024, the government announced an investment of $4.8 million over the next two years to expand the Starter Company Plus program. This enhancement will help an additional 500 entrepreneurs aged 18 and older to seed, start or grow a business by accessing one-on-one support, workshops, seminars or networking events, and grants of up to $5,000 through the program.
In May 2024, Ontario also announced an investment of $1.5 million to bolster its Summer Company program, helping an additional 250 young people start and grow a business. The Summer Company program provides students between the ages of 15 and 29 with at least 12 hours of business training, one‐on‐one mentoring, and grants up to $3,000 to start a full‑time business.
In addition, in June 2024, the government announced an investment of $500,000 over the next two years in the Fédération des gens d’affaires francophones de l’Ontario (FGA) to help Ontario’s Francophone entrepreneurs start or grow their businesses. In partnership with Small Business Enterprise Centres across the province, the FGA will offer free business advisory supports to Francophone entrepreneurs in the French language.

Attracting Entrepreneurs to the Province Through Horizon Ontario
To foster an innovative and productive economy, it is essential to provide a supportive environment that attracts dynamic talent and businesses and creates new opportunities for Ontario entrepreneurs. To support Ontario’s entrepreneurial growth, the government, through the Ontario Centre of Innovation, is providing up to $6 million over two years to the Toronto Business Development Centre (TBDC) to implement the Horizon Ontario program. This program will help attract European entrepreneurs to the province while supporting Ontario’s small and medium-sized enterprises to launch operations in Europe.
This follows Canada’s participation in Horizon Europe, a European Union (EU) research and innovation program that allows entrepreneurs to access opportunities and funding for collaborative research while strengthening relationships across economies. TBDC will assist Ontario entrepreneurs in accessing funding from the EU’s €95.5 billion funding program, as well as to provide business support services.
Helping Businesses Raise Capital
Ontario is focused on fostering greater competition and driving more innovative and cost-effective capital markets for Ontario businesses and investors. The government continues to support the Ontario Securities Commission (OSC) work to improve capital formation, promote innovation and ensure investor protection. In a recent C.D. Howe scorecard for financial regulation in Canada2, the OSC was singled out as the only securities regulator in Canada that is required to do a cost-benefit analysis when amending or adding new rules. This requirement underpins the government’s ongoing commitment to ensure innovative and cost-effective capital markets regulation:
- In spring 2024, the OSC introduced new measures that help increase access to capital for early-stage businesses and angel investor groups.
- In summer/fall 2024, the OSC consulted on rules to enable the implementation of the new distributions framework for disgorged funds to support more efficient, transparent and timely investor redress.
- The OSC’s ongoing engagement with Indigenous partners, including through the First Nations Economic Growth and Prosperity Table, to support better access to capital markets.
- The OSC’s ongoing work to modernize the dispute resolution framework to provide Ontario investors with an agile and binding dispute resolution framework through the Ombudsman for Banking Services and Investments (OBSI).
- The government is now proposing to enable the Canadian Public Accountability Board (CPAB) to implement new disclosure rules to strengthen transparency and accountability of CPAB inspections of audit firms.
- The government is also requesting that the OSC reviews its Offering Memorandum exemption, also known as OM exemption, to provide further capital formation opportunities.
The government supports the ongoing work by the OSC and the Canadian Investment Regulatory Organization (CIRO) to explore opportunities for strengthening Ontario’s short-selling framework and is looking forward to reviewing the findings of the CIRO working group.
Building Infrastructure, Highways and Transit in Your Communities
The strong growth of Ontario’s economy and population is putting extraordinary pressure on the province’s infrastructure. This, paired with years of underinvestment in these assets, has led to congestion and gridlock that costs families hours a week and is a drag on the economy. This is why the government remains focused on implementing the most ambitious capital plan in Ontario’s history. This historic infrastructure investment includes more than $191 billion over 10 years in highways, transit and other community infrastructure that the people of Ontario depend on. Still, there is more work to be done, and the government will continue to explore all available options to meet the needs of the economy and the people.
Getting Shovels in the Ground
The Building Ontario Fund Is Open for Business
The province requires more infrastructure than Ontario taxpayers alone can afford to finance. As the government moves forward with Ontario’s Plan to Build, the Building Ontario Fund (the Fund) is attracting capital from trusted Canadian institutional investors to help finance critical infrastructure projects across the province. This includes creating opportunities for pension funds to put their members’ investments to work right here in Ontario.

In its first year, the Fund has focused on achieving operational independence in order to move quickly to advance its mandate. The Fund recently announced its inaugural Chief Executive Officer and is recruiting other key executives. The Fund is developing a detailed investment framework to make meaningful investments in infrastructure and has an expert Board of Directors overseeing governance, operationalization, and execution of projects.
The Fund is advancing discussions with institutional investors, project proponents and government ministries. It now has a robust pipeline of outcome-focused projects in priority areas of energy, affordable housing, long-term care, municipal and Indigenous community infrastructure, and transportation, mobilizing institutional capital and prioritizing public benefits for the people of Ontario. Potential near-term investment opportunities include affordable student housing, energy, and long-term care projects.
Helping Municipalities and Communities Build Ontario
Ontario recognizes that municipalities are critical partners in delivering important local services and that by working together, the province and municipalities will build up Ontario’s communities and move its economy forward. Rising costs and historic underinvestment have made it hard for cities and towns to maintain roads, provide water, tackle congestion, fight crime and attend to the mental health needs of their residents.
In response, Ontario has taken meaningful actions to support and strengthen local communities with record investments in the municipal sector. In fact, from 2019 to 2023, key provincial support to municipalities grew by over 45 per cent. In 2023 alone, the government provided almost $10 billion through key programs. These investments include nearly $654 million annually through the Homelessness Prevention Program; increasing land ambulance funding to municipalities by an average of 6 per cent per year; investing almost $380 million through the Ontario Gas Tax Program to help municipalities operate and improve local transit; and investing an additional $1 billion for the Ontario Community Infrastructure Fund over five years, starting in 2022.
The province is supporting municipalities to enable housing growth through the Housing-Enabling Water Systems Fund (HEWSF), the Municipal Housing Infrastructure Program (MHIP), and the Building Faster Fund (BFF). The province is also investing $378 million to open 19 new Homelessness and Addiction Recovery Treatment (HART) Hubs and will add up to 375 supportive housing units as part of a comprehensive system of care that prioritizes community safety, recovery and prevention.
Looking ahead, the government will continue to work with municipalities to build more housing, support economic growth and further strengthen Ontario’s communities.
Supporting Ontario’s Largest Economic Centres
Toronto and Ottawa are unique economic engines in the provincial and national economies that face pressures and challenges that require additional support from all levels of government.
Through the New Deal with Toronto, Ontario is investing up to $1.2 billion in operating funding as well as significant capital supports to help achieve long-term financial sustainability for the city. Similarly, the Ontario–Ottawa agreement recognizes Ottawa’s unique social and economic challenges as the nation’s capital and Eastern Ontario’s economic hub, having faced a slower rebound from the effects of the pandemic. Through this agreement, Ontario is investing up to $543 million in the city.
These investments will benefit all the people of Ontario and strengthen the economy by helping to ensure the long-term growth, prosperity and public safety of these cities.
Supporting Small, Northern and Rural Communities
The government is committed to supporting the economic vitality and sustainability of Ontario’s small, Northern and rural municipalities. The government has heard about the financial challenges these municipalities face in delivering services to their communities. This is why the government will be increasing the Ontario Municipal Partnership Fund (OMPF) by $100 million over the next two years, bringing total funding provided through this program to $600 million by 2026. In 2025, municipalities will benefit from an immediate $50 million increase to the OMPF — the province’s main general assistance grant to municipalities.
The government plans to engage with municipalities on this important program. Beginning in the winter of 2025, the Ministry of Finance intends to consult with municipalities about their priorities for the program, as well as the implementation of a reporting framework in order to gain a better understanding of how the OMPF is supporting local communities.
Expanding High-Speed Internet Access to Unserved and Underserved Communities
The government is investing nearly $4 billion to provide access to high‐speed internet to every community across the province by the end of 2025. As of September 2024, over 100,000 previously unserved and underserved homes and businesses now have access to high‐speed internet. High‐speed internet allows people to access vital services like health care, learn from home, enhance their business, participate in the agricultural sector and connect with loved ones.
Multiple programs and initiatives are being used to meet this goal, many of which are well underway already, providing access to internet service and better cellular connectivity, including:
- Awarding contracts to eight internet service providers, through the provincial Accelerated High‐Speed Internet Program, which represents a diverse selection of local, regional and national carriers, to bring access to high‐speed internet to unserved and underserved areas;
- Advancing the Improving Connectivity for Ontario program and Universal Broadband Fund through co‐funded projects with the Government of Canada;
- Improving cellular access to numerous rural communities in Eastern Ontario with a provincial investment of $71 million in the Eastern Ontario Regional Network;
- Investing more than $63 million in the Southwestern Integrated Fibre Technology (SWIFT) project to bring high‐speed internet access to over 66,000 more homes, businesses and farms across Southwestern Ontario. To date, all 97 SWIFT projects are complete and in service;
- Investing $34 million in the SWIFT 2.0 project to capture additional premises within close proximity to work completed as part of SWIFT to provide high-speed internet access to a further 3,000 homes in Southwestern Ontario; and
- Investing $10.9 million to bring improved internet access to rural and First Nation communities across Northern Ontario.
Rebuilding Ontario Place
The rebuilding of Ontario Place is expected to create up to 5,000 construction and operations jobs and attract up to six million visitors annually. Anchor tenants will bring exciting family-friendly entertainment and activities to the site. The government is also working with Live Nation to create a year-round concert venue at Ontario Place. Once complete, Live Nation’s brand-new amphitheatre will welcome more fans to an all-season venue by increasing its capacity to up to 20,000 people while also protecting the much-loved amphitheatre lawn.
Therme Canada will create an all-season, family-friendly waterpark and wellness attraction that will include approximately 16 acres of new, publicly accessible parkland space, which will more than double the size of the existing Trillium Park.
In 2023, the province updated its development application to the City of Toronto to include:
- Approximately 50 acres of free parks, increased access to the waterfront, as well as public and green spaces for everyone to enjoy;
- A new, modernized Ontario Science Centre to be integrated with the preserved and upgraded Cinesphere and Pod complex;
- Additional waterfront programming, activity and play zones, and Indigenous elements and features throughout the site, as well as proposed Indigenous educational and programming opportunities;
- Public parking that will serve visitors across the site; and
- Improved mobility options such as upgrades to pedestrian bridges over Lake Shore Boulevard.
In May 2024, a Request for Qualifications was issued to identify a team that will design, build, finance and maintain the new Ontario Science Centre facility located at Ontario Place. The new state-of-the-art Ontario Science Centre facility will feature approximately 15 per cent more exhibit space than the previous site and will include interactive spaces for families, students and visitors to enjoy science-based exhibits and educational programming.
Funding Infrastructure to Build More Homes
One of the greatest barriers to building more homes is the need for more infrastructure connections, such as water, wastewater, electricity and roads. This is why the government is working with municipalities to invest nearly $2 billion in housing-enabling infrastructure funding to help build more homes across Ontario. This funding includes $1.22 billion for the Housing-Enabling Water Systems Fund and $725 million for the Municipal Housing Infrastructure Program. This funding complements existing and ongoing provincial investments in housing- and community-enabling infrastructure, including the Building Faster Fund and the Ontario Community Infrastructure Fund.
Supporting Municipalities with the Building Faster Fund
The province continues to work with municipalities as part of Ontario’s commitment to help unlock housing opportunities and support growing communities.
Announced in August 2023, the Building Faster Fund is designed to encourage municipalities to address the housing crisis. The fund rewards eligible municipalities that make significant progress against housing targets by providing funding for housing-enabling and community-enabling infrastructure. Funding is provided to eligible municipalities that have reached at least 80 per cent of their provincially assigned housing target for the year, with increased funding for municipalities that exceed their target. To date, municipalities have been awarded more than $260 million from the Building Faster Fund for their performance against their 2023 housing targets.

Implementing the Housing-Enabling Water Systems Fund
To enable the construction of more homes, the government increased investments for the Housing-Enabling Water Systems Fund (HEWSF) to $1.22 billion to help more municipalities repair, rehabilitate and expand drinking water, wastewater and stormwater infrastructure. The increased investment helps to respond to the significant demand for investments in water and wastewater infrastructure and includes $120 million from the Building Faster Fund that was reserved for small, rural and Northern communities.
Under the first intake for HEWSF, the province is investing $970 million in 54 water infrastructure projects across 60 municipalities that will help enable the construction of approximately 500,000 new homes across Ontario. The second intake of applications for $250 million was launched on August 14, 2024, and closes on November 1, 2024.
Ontario is also providing municipalities with improved and flexible borrowing terms for housing-enabling water projects under Infrastructure Ontario’s loan program. This lending stream would provide options to municipal partners, including small, rural and Northern municipalities. Options include deferred interest payments until projects are substantially complete, longer loan terms, more flexible repayment terms, and lower administration costs.
Launching the Municipal Housing Infrastructure Program
Building more homes is critical to Ontario’s economy and requires enabling infrastructure beyond just water. This is why the government announced the Municipal Housing Infrastructure Program (MHIP) to support core infrastructure projects. On August 20, 2024, the government launched the $400 million Housing-Enabling Core Servicing Stream for road and bridge infrastructure projects to enable more housing. This MHIP stream closed on October 18, 2024, and successful applicants will be notified in the coming months.
Lowering Taxes on Purpose-Built Rental Housing
Ontario welcomes the federal government’s decision to listen to Ontario’s long-standing call to provide Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) relief on new purpose-built rental housing projects.
The Ontario government has worked with the federal government to remove the full 8 per cent provincial portion of the HST on qualifying new purpose-built rental housing. Federal and provincial measures taken together remove the full 13 per cent HST on qualifying new purpose-built rental housing in order to get more rental homes built across the province.
The provincial portion of the HST is removed through the Ontario HST rebate for purpose-built rental housing, which is an enhancement of the HST new residential rental property rebate. The enhanced rebate applies to new purpose-built rental housing such as apartment buildings, student housing and senior residences built specifically for long-term rental accommodation and that meet eligibility criteria. The enhanced rebate applies to qualifying projects where construction began after September 13, 2023, but before 2031, and is substantially completed before 2036.
In addition, to further encourage the development of purpose‐built rental properties, the government announced in the 2024 Budget that it is providing municipalities with the flexibility to set their own reduced property tax rates on new multi‐residential rental properties. The Regional Municipality of York has already indicated that it plans to provide a reduced rate for these properties in 2025.
Building Roads and Highways to Fight Gridlock
The costs of congestion are real. Time stuck in traffic is one of the least productive parts of people’s day-to-day lives. It keeps people away from their families and delays the movement of goods for businesses. The Toronto Region Board of Trade estimates that gridlock costs the regional economy $11 billion every single year.
This is why the government is implementing the most ambitious capital plan in the province’s history, allowing Ontario to implement solutions for today, while exploring more options for the future. This includes investing $27.8 billion over the next 10 years to connect communities, fight gridlock and keep goods and people moving across the province. The Ontario Highways Program features 635 expansion and rehabilitation projects that are either underway or planned over the next four years. In 2024–25 alone, Ontario is investing almost $3.9 billion towards projects that will expand and repair provincial highways and bridges. The government is also ensuring that roads are being shared effectively and safely by enhancing oversight for new bike lanes.
Getting shovels in the ground on roads and highway projects today will help meet the future needs of a growing province, improve travel options, tackle gridlock and drive economic growth.
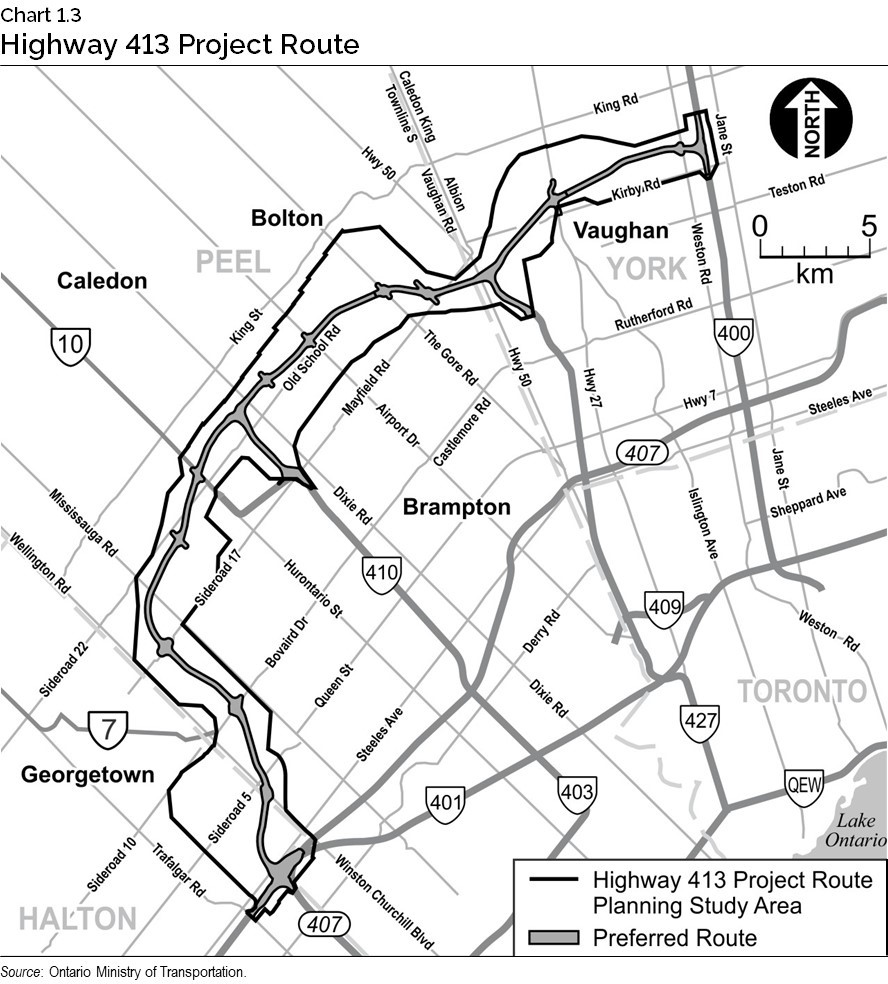
Highway 413
By 2051, the population in the Greater Golden Horseshoe is expected to reach nearly 15 million, growing by approximately one million new residents every five years. There is a pressing need for new highways to prepare for this growth and to help alleviate congestion on Highway 401 in what is already one of the busiest corridors in North America.
Ontario continues to move ahead with building Highway 413, a new 52-kilometre (km) 400-series highway to better connect the highway network across Halton, Peel and York Regions. The province is currently completing preliminary design of the whole corridor. The province has started expediting land acquisitions. In addition, the province is planning for the release of the first early works construction contracts to begin building Highway 413 in 2025, subject to all necessary approvals.
During construction, Highway 413 is expected to contribute $350 million to the province’s real GDP and support up to 3,500 jobs each year. Once completed, Highway 413 will save drivers up to 30 minutes each way on their commute during rush hour and keep goods and the economy moving.
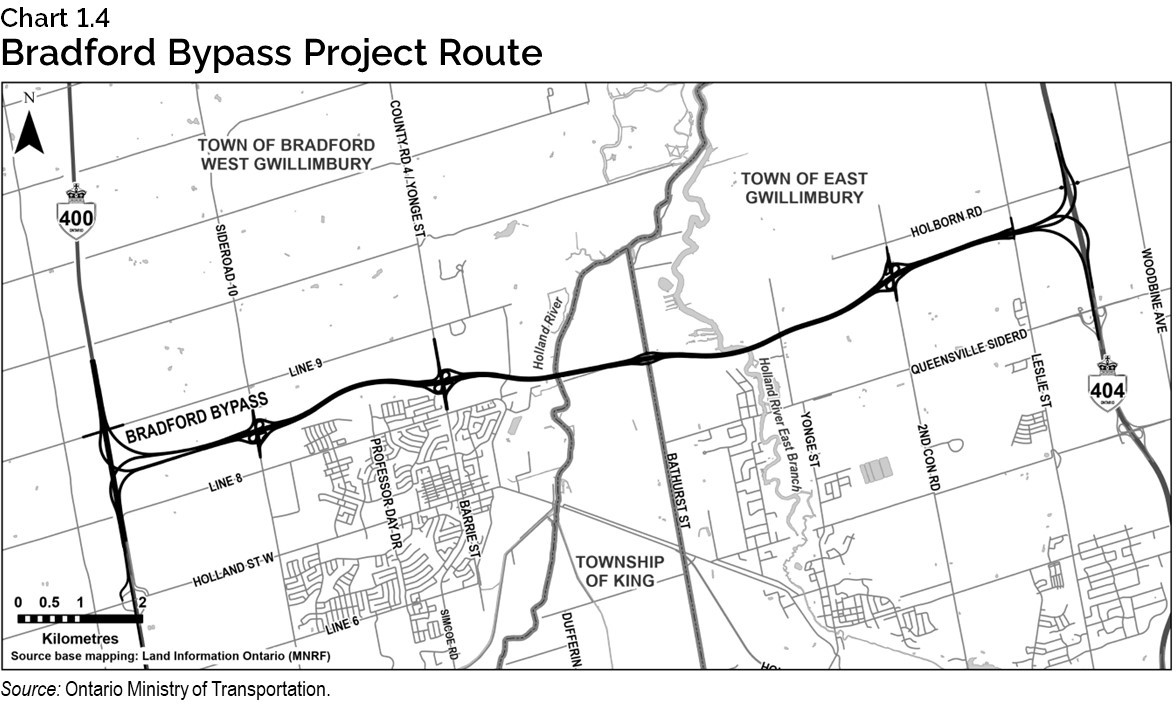
Bradford Bypass
Ontario is helping prepare York Region and Simcoe County for rapid population growth in the next 10 years by building the Bradford Bypass, a new four-lane highway to relieve congestion on existing east-west local roads and connect Highways 400 and 404. The new 16-kilometre highway will relieve gridlock, save commuters time, and keep goods moving across the Greater Golden Horseshoe.
In May 2024, the government awarded a contract for detail design of the west section of the Bradford Bypass, which will run 6.5 kilometres from Highway 400 to Simcoe County Road 4. In summer 2024, construction began on Highway 400 and the Simcoe County Road 88 bridge and interchange, which includes constructing a new southbound lane on Highway 400 that will connect to the future Bradford Bypass.
Once complete, the Bradford Bypass will save drivers an estimated 35 minutes in travel time compared to using local roads. During construction, the project is expected to create up to 2,200 jobs per year and contribute up to $286 million to the province’s GDP.
Expanding Highway 401
The Highway 401 corridor between the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) and Quebec is a crucial economic link within Ontario and between Ontario, Eastern Canada and the United States, handling about 11,000 trucks daily with goods valued up to $434 million.
The government is moving ahead with bridge replacements in Port Hope that will accommodate future widening of Highway 401. The government is also undertaking work to accommodate future expansion of Highway 401 in Durham Region. In summer 2024, construction began on the replacement of the Wilson Road overpass in the City of Oshawa. The new overpass will lay the groundwork for future widening of Highway 401.
This builds on the previous improvements of additional lanes on Highway 401 from Mississauga to Milton and from Highway 8 to Townline Road in Cambridge and helps tens of thousands of drivers daily in reaching their destinations faster and getting goods to market sooner.
Exploring a Highway 401 Tunnel Expressway
In addition to the work already being done to upgrade and expand the province’s 400-series highways, the government is exploring innovative options to tackle congestion. This is why, in September 2024, the government announced the launch of a feasibility study of a new driver and transit tunnel expressway under Highway 401. The feasibility work will examine various options to increase Highway 401 capacity, analyze the economic benefits both in the short and long term, as well as the project’s impact on reducing gridlock.
Twinning the Queen Elizabeth Way Garden City Skyway
The Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) Garden City Skyway Bridge Twinning project includes construction of a new bridge on the QEW over the Welland Canal, connecting the City of St. Catharines to the Town of Niagara‐on‐the‐Lake.
In April 2024, the government issued a Request for Proposals (RFP) to advance the project and invited five pre-qualified teams to bid on the project. This section of the highway supports tourism in Niagara Region, improves access to the Niagara District Airport and supports the province’s supply chain by linking the international border crossings at Niagara Falls and Fort Erie with the Greater Golden Horseshoe. The new and expanded Garden City Skyway will lead to less congestion and faster travel for people in the growing Niagara Region. The contract is expected to be awarded in spring 2025.
Building Highway 7
Construction of the new Highway 7 between Kitchener and Guelph will provide relief to the gridlocked Highway 401 and connect the fast‐growing urban centres of Kitchener, Waterloo and Guelph.
The government is advancing the project with activities that include replacement of the Frederick Street bridge in Kitchener, environmental field work, and other engineering work to support construction of the remainder of the corridor.
Additionally, the government is moving forward with planning and design work to expand Highway 7 from two to four lanes from west of Reesor Road in Markham, east to Brock Road in Pickering, to support the development of the City of Pickering’s Innovation Corridor. This will ensure Highway 7 is a continuous four‐lane highway from Markham to Pickering, supporting the movement of goods and people in the region.
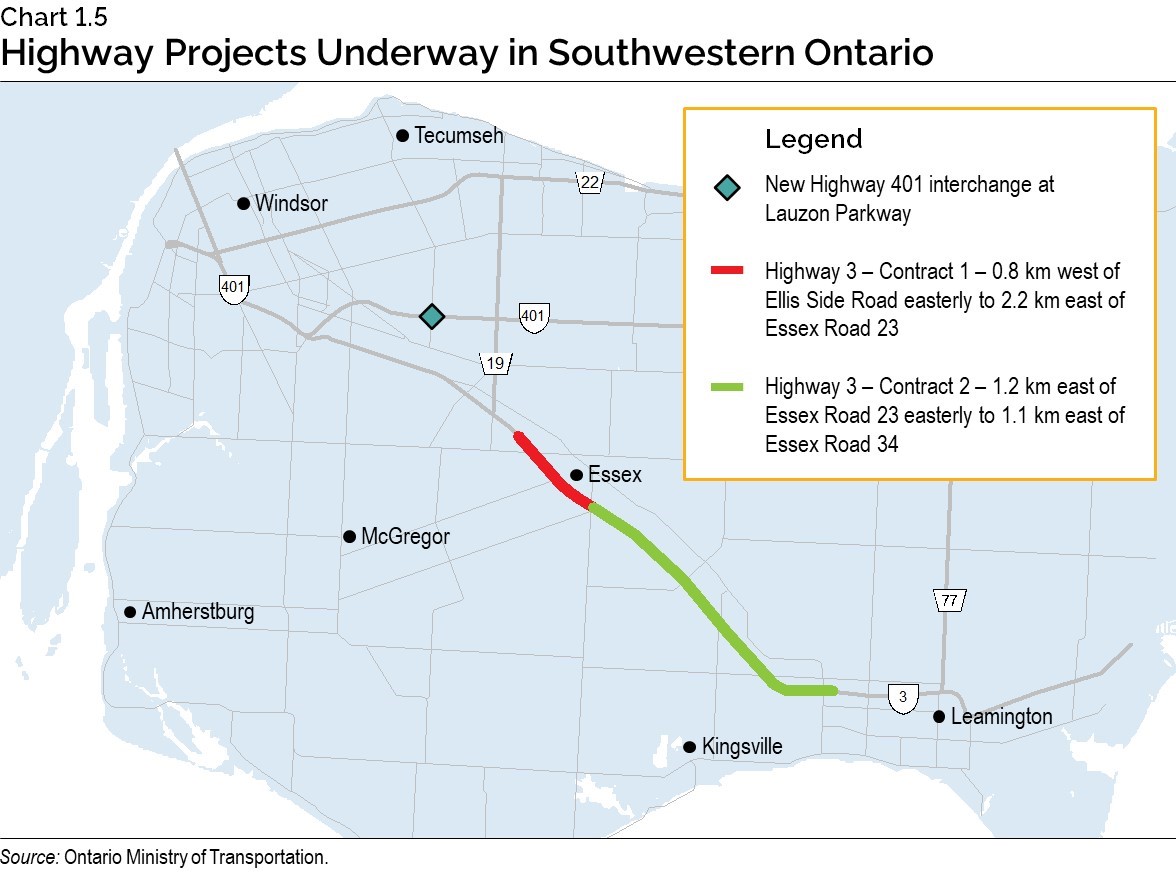
Investing in Highways in Southwestern Ontario
The government is continuing to improve road safety and keeping people and goods moving in Southwestern Ontario by starting construction to widen Highway 3 between Essex and Leamington.
The government has also procured a design consultant to complete Environmental Assessment and Preliminary Design for a new interchange connecting Highway 401 to the future Lauzon Parkway extension.
Advancing these critical transportation projects will increase economic growth and trade opportunities across Ontario’s border.

Building Highways for Northern Ontario
The government is investing in highways in the North to improve road safety, connect communities, and unlock economic opportunities. Projects include:
- Replacing the Little Current Swing Bridge on Highway 6 in the Town of Northeastern Manitoulin and the Islands. The planning, preliminary design and Environmental Assessment have been completed and the project is proceeding with the next steps — property acquisition, right‐of‐way designation and detail design.
- Working to increase passing opportunities on highways in Northeastern Ontario. This includes innovative designs such as a 2+1 highway, which is a three-lane highway with a centre passing lane that changes direction approximately every two to five kilometres.
- Expanding Highway 11/17 from two to four lanes between Thunder Bay and Nipigon, including from east of Highway 587 for 14.4 kilometres and from west of Highway 582 to Coughlin Road for 8.3 kilometres. These two projects are part of a larger series of projects to widen over 100 kilometres of the highway between Thunder Bay and Nipigon.
- Widening Highway 17 from Kenora to the Manitoba border. Section 1, which includes a 6.5‑kilometre segment from the Manitoba border easterly to west of Highway 673, will be completed in fall 2024. The broader project will widen Highway 17 from two to four lanes for approximately 40 kilometres.
- Supporting renewed partnerships with Animbiigoo Zaagi’igan Anishinaabek, Aroland First Nation, Ginoogaming First Nation and Long Lake #58 First Nation to build and improve highway infrastructure that will help connect more First Nation communities to the province’s highway network. This work includes maintenance and upgrades to Highway 584 and Highway 11, with work starting this construction season.

Building Capacity and Enhancing Road Safety Across Ontario
As part of the 635 expansion and rehabilitation projects planned or underway over the next four years of the Ontario Highways Program, the government is building capacity and enhancing road safety for travellers in every region of the province by:
- Continuing with construction of 10 new highway rest areas and rehabilitation of 14 existing rest areas, as announced in 2021, to better serve travellers along the provincial highway system;
- Completing work to replace 11 bridges in five locations along Highway 417 in Ottawa. This work includes the rapid replacement of both eastbound and westbound bridges from Island Park Drive to Kent Street. Preliminary and detail design work is underway for the replacement of additional bridges along the Ottawa Queensway, with the next construction project expected to begin in 2025; and
- Improving Highway 401 near Kingston by resurfacing sections of the eastbound and westbound lanes on Highway 401 from Westbrook Road to Highway 15, along with all four ramps at the Sir John A. Macdonald interchange.
Table 1.1
Recently Completed Highway Projects
Northern
- Resurfacing of Highway 11, from 17.4 km north of the west junction of Highway 583 to Highway 663.
- Resurfacing of Highway 101 from Highway 7172 (Foleyet) westerly.
- Resurfacing of Highway 69, from 2.3 km south of the Nelson Road Interchange to 1.3 km south of Crown Ridge Road, Sudbury.
- Rehabilitation of Highway 631 and Highway 11, west of Highway 631 easterly.
Eastern
- Bay of Quinte Skyway Bridge: Bridge rehabilitation to serve as an important connection to Highway 401 for Prince Edward County.
- Highway 17 – Harvey Creek Road to Stonecliffe resurfacing.
- Highway 401 – County Road 2 to Maitland Road, eastbound/westbound resurfacing.
- Middle Road Maintenance Patrol Yard – New Building/Garage (located off Highway 401 and Highway 15 interchange, Kingston).
Southwestern
- Highway 3 pavement rehabilitation from Cayuga to Haldimand Road 56, Canfield.
- Highway 401 Wonderland Road interchange South Ramp Terminal, traffic signals.
- Highway 402 Kerwood to Hickory Drive – safety improvements.
- Highway 402 pavement resurfacing, Middlesex Road 2 (Longwoods Drive) to Colonel Talbot Road, Middlesex County.
Central
- Highway 404 widening and new High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lane from Highway 407 to Stouffville Road.
- QEW/Highway 403 Freeman Interchange bridge rehabilitations.
- Highway 403 at Trinity, Shaver and Alberton Roads and Sunnyridge bridge rehabilitations and roundabouts (anticipated completion October 2024).
- Highway 7 Silver Creek and Credit River bridge rehabilitations.
Source: Ministry of Transportation.
Fighting Gridlock by Requiring Municipalities to Get Approval for New Bike Lanes
The government is helping drivers move faster and bringing balance back to bike lane decisions by introducing legislation that would, if passed, allow the province to remove existing bike lanes, and require municipalities to receive approval from the province before installing new bike lanes that would result in the removal of lanes for traffic.
Building Transit
Ontario cannot tackle gridlock with roads and highways alone. Public transit projects are also vital to support the province’s economy and connect more people to jobs and housing. Transit investment has not kept up with growth, which is why the province is leading the largest expansion of public transit in North America. But there is more work to be done as Ontario’s cities and towns continue to grow at historic rates.
Expanding GO Transit Services
To better connect growing communities across the Greater Golden Horseshoe, the government is continuing to expand and build better GO train and GO bus services to make it easier and faster for people to get where they need to go.
Ontario continues to invest in service and capacity improvements across the core network to bring two-way, all-day GO Transit service with faster trains, more stations and better connections.
The government has moved ahead with the largest GO train service expansion in more than a decade by adding more than 300 trips per week on the Milton, Lakeshore West, Lakeshore East, Kitchener and Stouffville lines.
- Kitchener GO Line: To enable two-way, all-day service on the Kitchener Line, improvements are being made to stations and the railway corridor. In Guelph, work on the new train platform will be completed in 2024.
- Bloor GO Station: In May 2024, construction began on the new pedestrian tunnel connecting the Bloor GO/UP Express Station and the Toronto Transit Commission Dundas West Station. This connection will encourage travellers to choose to combine GO Transit or UP Express trips with TTC subway, streetcar or bus services, and support the growth of a more interconnected regional rapid transit network.
- Caledonia GO Station: In October 2024, a contract was awarded for the construction of the new Caledonia GO Station on the Barrie Line. This new station will provide seamless connections between trains on the Barrie Line, the Eglinton Crosstown Light Rail Transit (LRT), and TTC buses — providing better transit within the region.
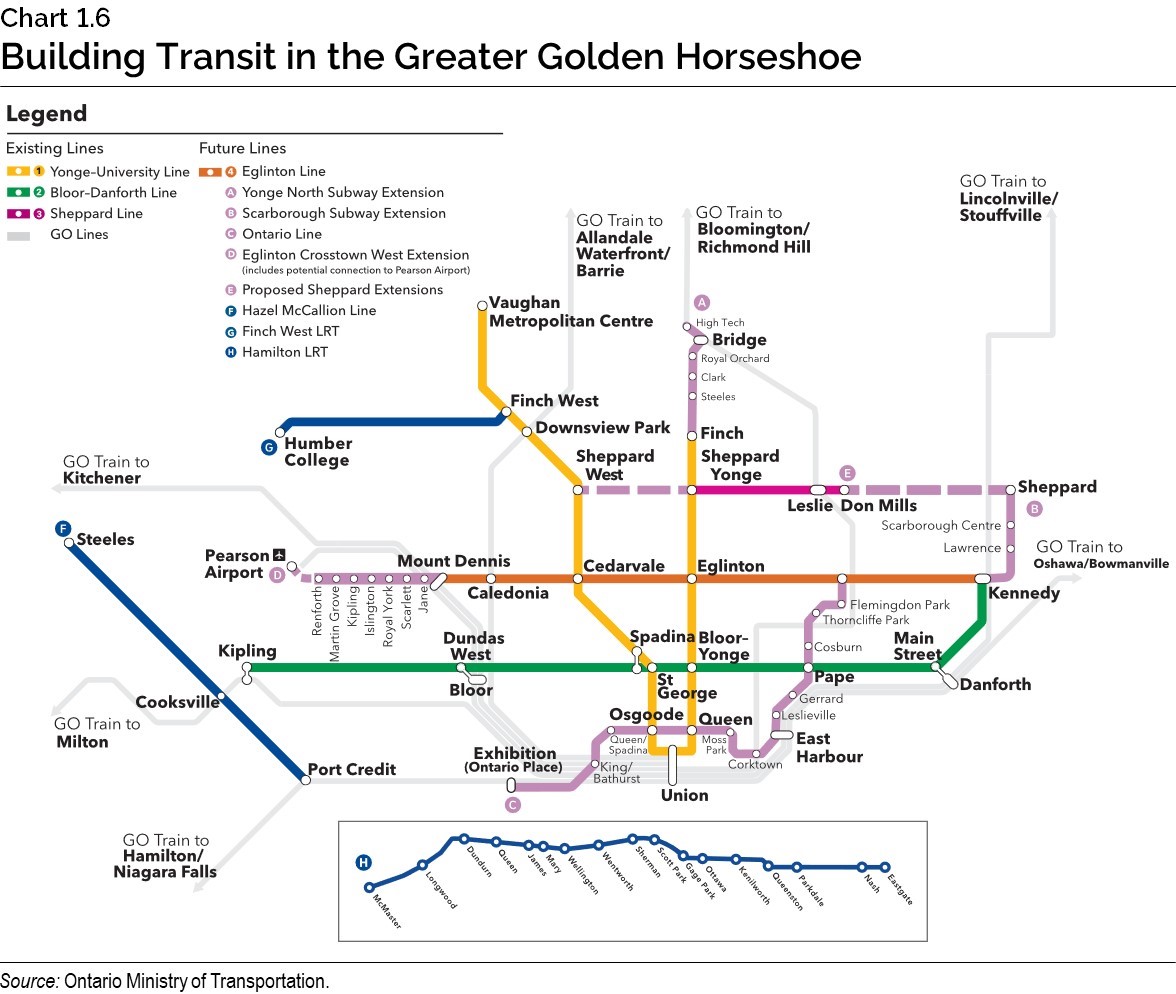
Building Subways
Work is underway on all four of Ontario’s priority subway projects. The government is closer to providing better travel options, alleviating gridlock on the roads and creating thousands of good, local jobs.
The combined subway projects will support more than 16,000 jobs annually during construction over the next decade. Shovels are in the ground and recent milestones include:
- Ontario Line: Construction is now underway across the entire Ontario Line, marking a significant milestone in the province’s plan to bring nearly 230,000 people within walking distance of fast and convenient public transit. The government has officially broken ground at Pape Station, marking the start of construction to build a new interchange station, connecting the Ontario Line with TTC Line 2 (Bloor–Danforth). The government has also broken ground at the King-Bathurst, Queen-Spadina and Moss Park Stations. In January 2024, Metrolinx and Infrastructure Ontario (IO) entered into the development phase with the preferred proponent for the Pape Tunnel and Underground Stations and the Elevated Guideway and Stations contracts. The project will provide significant relief from crowding throughout the existing transit network, with 388,000 daily boardings expected, and will reduce traffic congestion with 28,000 fewer cars on the road expected daily.
- Scarborough Subway Extension: The project is expected to handle 105,000 daily boardings and provide transit access within walking distance to 38,000 more people. The Stations, Rail and Systems Contract development phase with the preferred proponent continues to progress. This contract includes design and construction of three new underground stations and bus terminals at each station.
- Yonge North Subway Extension: In December 2023, the government issued an RFP for the Advance Tunnel Contract that includes work to design, build and finance the construction of tunnels. The advance tunnelling RFP has been issued to shortlisted bidders for design, build and finance proposals. Early upgrade work at Finch Station, where the Yonge North Subway Extension will connect with existing Line 1 service, is now substantially complete. The upgrades set the stage for major construction of the subway extension to Richmond Hill and Markham.
- Eglinton Crosstown West Extension: Tunnelling of the western underground portion of the Eglinton Crosstown West Extension has finished, marking a significant milestone in the project. As of June 24, 2024, major tunnelling for the Advance Tunnel Contract 1 is complete and both tunnel boring machines have been extracted. Contracts were awarded for the elevated guideway portion in December 2023 and the Advance Tunnel 2 project in February 2024. In March 2024, a Request for Qualifications was issued for the design and construction of seven stations along the Eglinton Crosstown West Extension.
- Proposed Sheppard Subway Extension: The government is advancing planning and conducting community consultations on options to extend rapid transit both east and west of the existing TTC Line 4, which would improve transit connections in Toronto’s north end and make it easier and faster for people to get around Toronto and the GTA.

Building and Expanding Light Rail Transit
The government is bringing fast, reliable transit projects to help reduce travel times and create more transit options, including:
- Finch West LRT: The project has reached a number of important milestones with the completion of all major construction, including all stations and stops. The project is now undergoing testing and commissioning in preparation for revenue service. This LRT from Humber College to Finch West Station will give those in Northwest Toronto a transit system that offers more choices to travel, cuts down on travel time and increases transit reliability.
- Eglinton Crosstown LRT: Since spring 2024, significant progress has been made towards the goal of opening the line. Nearly all occupancy permits have been received from the City of Toronto. The project is currently in the testing and commissioning phase, which will ensure the line works safely and reliably for customers.
- Hamilton LRT: Progress continues to be made on the enabling works program, including utility relocations in preparation for future stages of construction.
Bringing Back the Northlander
Ontario is delivering on its promise to restore passenger rail service to Northern Ontario. The Northlander train will provide a safe and reliable transportation option for Northern communities.
As part of this commitment, Ontario has purchased three new trainsets for the reinstated service. In May 2024, the government awarded three contracts to design and manufacture nine new station shelters, enhance rail safety and complete warning system upgrades, with construction underway.
The Northlander train will provide improved access to essential services such as health care and education, while supporting economic prosperity and tourism in the region, as well as strengthening the connection between Northern and Southern Ontario.
Launch of the Ontario Transit Investment Fund
The government has officially launched the Ontario Transit Investment Fund (OTIF). This new, annual fund of $5 million will address transit service gaps by supporting the startup and growth of transit services in unserved and underserved communities across the province. OTIF will include an ongoing application-based intake. Through OTIF, municipalities, Indigenous communities and non-profit organizations will lead project teams consisting of key partners to develop integrated, coordinated and sustainable transit services.
Chart Descriptions
Chart 1.1: Top Five U.S. Destinations for Ontario Exports in 2023
This chart illustrates Ontario’s top five export destinations within the United States in 2023. Ontario domestic exports are on a customs basis and are denoted in Canadian dollars. In 2023, the top destination for Ontario’s exports within the United States was Michigan ($52.9 billion), followed by Texas ($26.7 billion), New York ($16.1 billion), Illinois ($12.1 billion) and Ohio ($11.6 billion).
Source: Statistics Canada.
Chart 1.2: Supporting Ontario Businesses
This bar chart illustrates that Ontario businesses are expected to receive $7.9 billion in estimated cost savings and support in 2024. This includes combined support from lowering payroll costs ($3.4 billion), providing electricity and other price relief ($1.7 billion), providing income and property tax relief ($1.0 billion), and cancelling the cap-and-trade carbon tax ($1.7 billion).
Notes: Lowering payroll costs includes supporting Workplace Safety and Insurance Board (WSIB) premium reductions, increasing the Employer Health Tax (EHT) exemption to $1 million starting 2020 and changing the minimum wage. Providing electricity and other price relief represents lowering electricity prices through the Comprehensive Electricity Plan; reducing Liquor Control Board of Ontario (LCBO) wholesale prices for bars, restaurants and other eligible licence holders; and the direct savings to businesses from extending the 5.7 cent per litre cut to the gas tax and the 5.3 cent per litre cut to the fuel tax until December 31, 2024. Providing income and property tax relief includes reducing Ontario’s small business corporate income tax rate to 3.2 per cent and expanding access to this preferential rate; allowing businesses to accelerate writeoffs of capital investments for income tax purposes; implementing the Regional Opportunities Investment Tax Credit; implementing the Ontario Made Manufacturing Investment Tax Credit; lowering high Business Education Tax (BET) rates; and not paralleling the federal tax increase on some small businesses earning passive investment income. Categories may not add due to rounding.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Finance.
Chart 1.3: Highway 413 Project Route
The image shows a map of the Highway 413 Project Route of the planning study area and the Preferred Route.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Transportation.
Chart 1.4: Bradford Bypass Project Route
The image shows a map of the Bradford Bypass Project Route. The bypass will run between Highway 400 and Highway 404, passing through the Town of Bradford West Gwillimbury and the Township of King.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Transportation.
Chart 1.5: Highway Projects Underway in Southwestern Ontario
The image shows a map of Southwestern Ontario, highlighting highway projects underway, including the new Highway 401 interchange at Lauzon Parkway, Highway 3 Contract 1 location and Highway 3 Contract 2 location.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Transportation.
Chart 1.6: Building Transit in the Greater Golden Horseshoe
This image shows a map of subway lines in the Greater Golden Horseshoe, including current lines, expansion projects that are underway, and proposed future expansions.
Source: Ontario Ministry of Transportation.
Footnotes
[1] Statistics Canada, Survey of Employment, Payrolls and Hours, https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/t1/tbl1/en/cv.action?pid=1410020201
[2] Paul C. Bourque & Gherardo Gennaro Caracciolo, The Good, the Bad and the Unnecessary: A Scorecard for Financial Regulations in Canada (C.D. Howe Institute, 2024), https://www.cdhowe.org/sites/default/files/2024-07/Commentary_664_0.pdf